In today’s dynamic business landscape, achieving a sustainable competitive advantage is paramount for long-term success. One proven path to this success is through cost leadership, a strategy focused on becoming the lowest-cost producer in an industry while maintaining acceptable quality. This exploration delves into the core principles of cost leadership, examining how businesses can identify and reduce costs, optimize supply chains, leverage technology, and ultimately translate cost efficiency into higher profitability and market share.
We will also explore the potential risks and challenges associated with this approach, alongside alternative competitive strategies.
Understanding the nuances of cost leadership involves more than just slashing expenses; it requires a holistic approach that integrates efficient operations, strategic supply chain management, and technological innovation. This strategy is not without its complexities; maintaining a cost leadership position requires constant vigilance, adaptation to market shifts, and a keen understanding of the competitive landscape. This examination will provide a comprehensive overview, equipping readers with the knowledge to assess the viability and implications of adopting a cost leadership strategy within their own business context.
Defining Cost Leadership
Cost leadership, a fundamental competitive strategy, focuses on achieving the lowest cost of production and distribution within an industry while maintaining acceptable quality. This allows a company to offer its products or services at a lower price than competitors, attracting price-sensitive customers and gaining a significant market share. Successfully implementing this strategy requires operational efficiency, economies of scale, and a keen understanding of cost drivers.Cost leadership hinges on several core principles.
First, it requires a relentless pursuit of efficiency in all aspects of the business, from procurement and manufacturing to marketing and distribution. Second, it emphasizes economies of scale, meaning that the larger the production volume, the lower the average cost per unit. Third, a deep understanding of cost drivers – the factors that influence the overall cost structure – is crucial for identifying areas for improvement and cost reduction.
Finally, maintaining acceptable quality is paramount; simply offering the cheapest product isn’t enough if it’s inferior and fails to meet customer expectations.
Industries Where Cost Leadership is Dominant
Cost leadership is particularly prevalent in industries characterized by standardized products or services with low switching costs for consumers. Examples include fast fashion, where companies like Shein compete fiercely on price; commodity markets like steel or agricultural products; and budget airlines, where companies such as Ryanair focus on maximizing efficiency to offer incredibly low fares. In these industries, price is often the primary driver of consumer choice.
Key Factors Contributing to Cost Leadership
Several key factors contribute to achieving a cost leadership position. These include efficient supply chain management, leveraging technological advancements to automate processes and reduce labor costs, optimizing production processes, and negotiating favorable terms with suppliers. Furthermore, a strong focus on lean manufacturing principles, which aim to eliminate waste and maximize efficiency, is crucial. Access to low-cost resources, such as raw materials or labor, can also provide a significant advantage.
Finally, effective cost accounting and control systems are essential for monitoring performance and identifying areas for improvement.
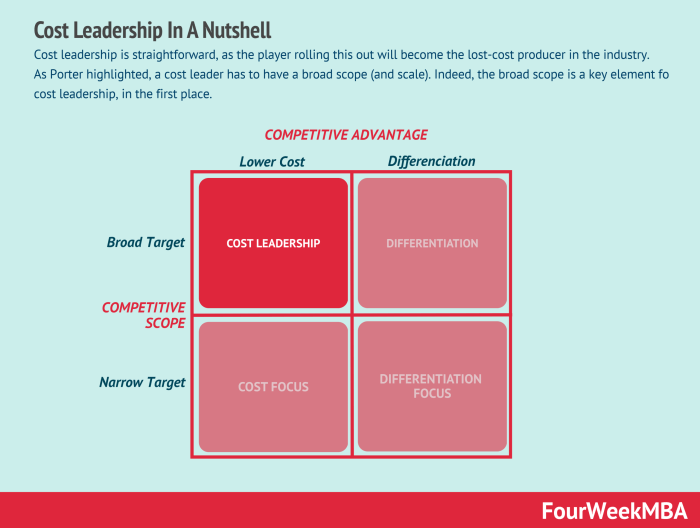
Comparison of Cost Leadership with Other Competitive Strategies
| Feature | Cost Leadership | Differentiation | Focus (Niche) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Competitive Advantage | Low Price | Unique Product/Service | Specific Customer Needs |
| Target Market | Price-sensitive consumers | Customers willing to pay a premium | A particular segment of the market |
| Value Proposition | Best value for money | Superior quality, features, or brand image | Specialized solutions tailored to a niche |
| Risks | Price wars, imitation, cost reduction exceeding acceptable quality | High R&D costs, changing customer preferences | Limited market size, dependence on a single segment |
Achieving Cost Leadership
![]()
Achieving cost leadership requires a multifaceted approach that integrates operational efficiency, strategic supply chain management, and technological innovation. It’s not simply about cutting corners; it’s about systematically identifying and eliminating waste while maintaining or improving quality and service. A successful cost leadership strategy demands a continuous improvement mindset and a deep understanding of the business’s cost structure.
Identifying and Reducing Operational Costs
Effective cost reduction begins with a thorough understanding of where the money is being spent. This involves detailed cost accounting, identifying areas of inefficiency, and prioritizing areas for improvement. A systematic approach, such as value engineering, can be employed to analyze every aspect of the production process, identifying non-value-added activities and eliminating them. For example, a manufacturing company might identify that a specific step in its assembly line is redundant and can be removed, thereby reducing labor and material costs.
Furthermore, streamlining internal processes, negotiating better terms with suppliers, and implementing energy-efficient technologies can all contribute to significant cost savings. Regular performance reviews and benchmarking against industry best practices can help identify further areas for improvement.
Optimizing Supply Chain Management for Lower Costs
The supply chain represents a significant portion of a company’s overall costs. Optimizing this area is crucial for achieving cost leadership. This involves several key strategies. First, establishing strong relationships with reliable suppliers can lead to better pricing and more efficient delivery. Second, implementing just-in-time (JIT) inventory management minimizes storage costs and reduces the risk of obsolescence.
Third, exploring alternative sourcing options, such as nearshoring or reshoring, can lower transportation costs and lead times. Finally, utilizing advanced analytics and supply chain visibility tools can improve forecasting accuracy, optimize inventory levels, and reduce waste. For instance, a retailer using predictive analytics might accurately forecast demand, preventing overstocking and associated storage and disposal costs.
The Role of Technology in Achieving Cost Leadership
Technology plays a vital role in driving down costs across various aspects of the business. Automation, for example, can significantly reduce labor costs and improve efficiency in manufacturing and other processes. Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems can streamline operations, improve data visibility, and reduce administrative overhead. Data analytics tools can help identify cost-saving opportunities that might otherwise go unnoticed.
Investing in advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) can further optimize processes and predict future cost trends, allowing for proactive cost management. For example, AI-powered predictive maintenance can reduce downtime and repair costs by anticipating equipment failures before they occur.
Evaluating the Effectiveness of Cost Reduction Initiatives
A robust evaluation process is critical to ensure that cost reduction initiatives are delivering the desired results. This involves setting clear, measurable goals and regularly tracking key performance indicators (KPIs). These KPIs should align with the specific cost reduction objectives and include metrics such as unit cost, operating expenses, inventory turnover, and supply chain efficiency. Regular reporting and analysis of these KPIs provide valuable insights into the effectiveness of implemented strategies.
Furthermore, conducting post-implementation reviews allows for identifying areas for improvement and adapting strategies as needed. This iterative approach ensures that cost reduction efforts remain effective and aligned with the company’s overall strategic goals. For instance, tracking the return on investment (ROI) for each cost reduction initiative helps determine its overall success and inform future decisions.
Competitive Advantage through Cost Leadership

Cost leadership, as a competitive strategy, offers a powerful pathway to achieving significant market share and superior profitability. By meticulously managing costs across all aspects of the business, firms can offer products or services at lower prices than competitors, thereby attracting price-sensitive customers and potentially driving out less efficient rivals. However, this approach isn’t without its challenges and inherent risks.
Understanding both the advantages and drawbacks is crucial for successful implementation.
Benefits and Risks of Cost Leadership
A cost leadership strategy, when successfully executed, yields numerous benefits. These include increased market share due to lower prices, higher profit margins resulting from efficient operations, and a stronger competitive position against rivals. However, focusing solely on cost reduction can also present significant risks. These include a potential for reduced product quality or innovation if cost-cutting measures compromise essential elements of the product or service, and vulnerability to changes in input costs, such as raw materials or labor, which can erode profit margins.
Additionally, a relentless pursuit of cost reduction may damage brand image or customer loyalty if perceived quality suffers. A carefully balanced approach is therefore essential.
Sustainability of Cost Leadership Across Market Environments
The sustainability of a cost leadership strategy varies considerably depending on the market environment. In stable, mature markets with relatively predictable demand, a cost leadership position can be highly sustainable, as firms can focus on long-term efficiency improvements. However, in dynamic, rapidly changing markets characterized by technological innovation or fluctuating consumer preferences, maintaining a cost leadership position becomes more challenging.
Continuous innovation and adaptation are essential to avoid being overtaken by competitors with more agile or innovative approaches. Furthermore, industries with high barriers to entry (e.g., significant capital requirements) tend to favor cost leadership strategies, as new entrants face difficulties competing on price.
Cost Leadership, Profitability, and Market Share
Cost leadership directly translates into higher profitability and increased market share. Lower production costs allow firms to offer lower prices, making their products or services more attractive to price-sensitive consumers. This increased demand leads to higher sales volume, which, combined with lower costs per unit, results in greater profitability. Simultaneously, capturing a larger segment of the market through competitive pricing increases market share, further strengthening the firm’s position.
This virtuous cycle of cost reduction, increased sales, and higher profits solidifies the competitive advantage.
Case Study: Walmart’s Cost Leadership Strategy
Walmart provides a compelling example of a company that successfully achieved a competitive advantage through cost leadership. Their success can be attributed to several key steps:
- Efficient Supply Chain Management: Walmart implemented a highly efficient and sophisticated supply chain, utilizing advanced logistics and technology to minimize transportation costs and inventory holding costs. This involved developing strong relationships with suppliers and optimizing distribution networks.
- Economies of Scale: Walmart’s vast network of stores and high sales volume allowed them to leverage economies of scale, negotiating lower prices from suppliers and spreading fixed costs over a larger number of units.
- Cost Control Across Operations: Walmart rigorously managed costs across all aspects of its operations, from staffing and store design to marketing and advertising. This included minimizing labor costs through efficient scheduling and automation.
- Everyday Low Prices Strategy: Walmart’s commitment to “everyday low prices” became a powerful brand differentiator, attracting price-conscious consumers and creating a strong barrier to entry for competitors.
Sustaining Cost Leadership
Maintaining a cost leadership position requires ongoing vigilance and adaptation. The competitive landscape is constantly shifting, with new technologies, evolving consumer preferences, and aggressive competitors all vying for market share. Simply achieving cost leadership is not enough; businesses must actively work to sustain this advantage to ensure long-term profitability and success.
Challenges in Maintaining Cost Leadership
Sustaining cost leadership presents several significant hurdles. Competitors may aggressively undercut prices, forcing companies to reduce their margins or risk losing market share. Technological advancements can disrupt established processes, rendering existing cost-saving measures obsolete. Furthermore, unexpected economic downturns or supply chain disruptions can significantly impact a company’s cost structure, eroding its competitive edge. Finally, a relentless focus on cost reduction can sometimes lead to neglecting innovation or customer service, potentially weakening the overall brand and market position.
Examples of Companies Losing Cost Leadership
Several companies have lost their cost leadership advantage due to various factors. For instance, Kodak, once a dominant player in the photography industry, failed to adapt to the rise of digital photography, losing its cost advantage and ultimately filing for bankruptcy. Their inability to innovate and embrace new technologies rendered their established cost-reduction strategies irrelevant. Similarly, some major retailers have struggled to compete with online giants like Amazon, which have leveraged technology and scale to achieve significantly lower costs and offer competitive pricing.
These examples highlight the importance of proactive adaptation and continuous innovation in maintaining a cost leadership position.
Strategies for Adapting to Changing Market Conditions
Adapting to market changes while preserving cost leadership necessitates a multi-pronged approach. Companies need to invest in research and development to identify and adopt new technologies that enhance efficiency and reduce costs. They should also continuously analyze their supply chains to identify potential cost savings through optimization and strategic sourcing. Moreover, fostering strong relationships with suppliers is crucial for securing favorable pricing and reliable supply.
Finally, investing in employee training and development is essential to improve productivity and reduce operational errors. A proactive approach to risk management, including scenario planning for potential disruptions, is also crucial.
Proactive Management of Cost Leadership: A Flowchart
The following flowchart illustrates a proactive approach to managing cost leadership:[Diagram Description: The flowchart begins with a “Start” node. It then branches into three main processes: Continuous Cost Analysis, Process Optimization, and Strategic Partnerships. Continuous Cost Analysis involves regularly reviewing all aspects of the cost structure, identifying areas for improvement, and implementing cost-reduction measures. Process Optimization focuses on streamlining operations, improving efficiency, and adopting new technologies to reduce costs.
Strategic Partnerships involve building strong relationships with suppliers and other stakeholders to secure favorable pricing and reliable supply. Each of these processes feeds back into a central “Review and Adjust” node, where the effectiveness of the implemented strategies is evaluated and adjustments are made as needed. The flowchart concludes with an “End” node. The overall flow is cyclical, emphasizing the ongoing nature of cost leadership management.]
Competitive Advantage
Cost leadership, while a powerful strategy, isn’t the only path to competitive advantage. A company’s success hinges on understanding its market and choosing a strategy that aligns with its capabilities and the competitive landscape. Beyond minimizing costs, businesses can thrive by offering unique value propositions that resonate with specific customer segments.
Types of Competitive Advantage Beyond Cost Leadership
Differentiation and niche strategies represent significant alternatives to cost leadership. Differentiation focuses on creating products or services perceived as unique and superior, justifying a premium price. Niche strategies target a specific, underserved market segment with specialized offerings. These strategies leverage different aspects of the value chain to generate competitive advantage, moving beyond simple cost reduction.
Examples of Differentiation and Niche Strategies
Apple, for example, has consistently achieved competitive advantage through differentiation. Its products are known for their design, user experience, and brand prestige, commanding higher prices than competitors. Conversely, a company specializing in organic, locally-sourced food products would represent a niche strategy, catering to a specific consumer segment willing to pay a premium for sustainability and quality. These examples highlight how focusing on specific aspects of value—whether it’s brand image or product specialization—can lead to sustainable competitive advantage.
Comparing and Contrasting Approaches to Sustainable Competitive Advantage
Sustainable competitive advantage requires creating barriers to imitation. Cost leadership strives to create this barrier through economies of scale, efficient operations, and technological innovation. Differentiation relies on building strong brands, creating unique product features, and fostering customer loyalty. Niche strategies achieve sustainability by developing deep expertise and strong relationships within their chosen market segment, making it difficult for larger competitors to effectively compete.
Each approach demands a unique set of resources and capabilities, making the choice of strategy crucial for long-term success. A direct comparison reveals that while cost leadership focuses on efficiency, differentiation emphasizes uniqueness, and niche strategies emphasize specialization.
The Importance of Understanding the Competitive Landscape
Choosing the right competitive strategy is inextricably linked to understanding the competitive landscape. A thorough analysis of the industry structure, competitor actions, and market dynamics is crucial. For instance, a highly competitive market with low barriers to entry might favor a cost leadership approach, while a market with strong brand loyalty and differentiated products may be more suitable for a differentiation strategy.
A niche strategy, on the other hand, is often most effective in markets with fragmented demand or specialized customer needs. Ignoring the competitive landscape can lead to strategic misalignment and ultimately, failure. Careful analysis ensures a strategy’s fit with the market environment, increasing the likelihood of success.
Ultimately, achieving and sustaining a competitive advantage through cost leadership demands a multifaceted and strategic approach. While the potential rewards—increased profitability, expanded market share, and enhanced customer value—are significant, businesses must carefully consider the inherent risks and challenges. Successful implementation requires a commitment to operational efficiency, continuous improvement, technological advancement, and a proactive response to evolving market dynamics. By understanding the core principles, potential pitfalls, and innovative applications of cost leadership, businesses can effectively navigate the competitive landscape and build a foundation for lasting success.
Key Questions Answered
What are some examples of companies that have successfully employed cost leadership?
Walmart, McDonald’s, and IKEA are often cited as examples of companies that have achieved significant success through cost leadership strategies.
Can a company simultaneously pursue cost leadership and differentiation?
While challenging, some companies successfully pursue both. This often involves focusing on cost efficiencies in certain areas while investing in differentiation in others (e.g., offering superior customer service while maintaining low prices).
How can a company measure the effectiveness of its cost reduction initiatives?
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) such as cost per unit, operating margin, and return on assets can be used to track the effectiveness of cost reduction efforts. Regular benchmarking against competitors is also crucial.
What are the ethical considerations of cost leadership?
Ethical considerations include ensuring fair labor practices, avoiding environmental damage, and maintaining product quality even while minimizing costs. A purely cost-focused approach can lead to ethical compromises.