In today’s rapidly evolving business landscape, leveraging technology is no longer a luxury but a necessity for sustained competitive advantage. The ability to harness technological advancements to optimize operations, innovate products, and enhance customer experiences is paramount for success. This exploration delves into the multifaceted ways technology shapes modern competition, examining its impact across various organizational functions and future implications.
From streamlining supply chains through automation to utilizing data analytics for predictive modeling, technology offers a diverse toolkit for businesses seeking to outpace rivals. We will investigate how companies are utilizing these tools, analyzing both the strategic benefits and the potential risks associated with technological adoption. The ultimate goal is to understand how a strategic and well-executed technology plan translates into a robust and sustainable competitive edge.
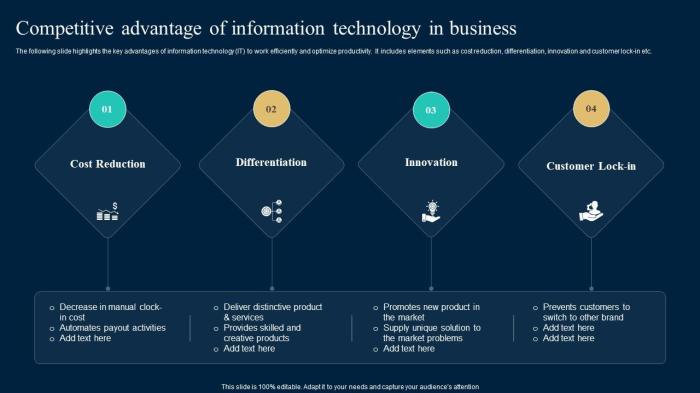
Defining Competitive Advantage
A competitive advantage represents a firm’s ability to outperform its rivals and achieve superior profitability. It’s not simply about making a profit; it’s about consistently generating higher profits than competitors over a sustained period. This advantage stems from offering greater value to customers, operating more efficiently, or possessing resources that competitors lack. Achieving and maintaining this edge is the ultimate goal for any business striving for long-term success.A sustainable competitive advantage, however, is a more robust and enduring form of advantage.
It’s built upon factors that are difficult for competitors to imitate or replicate. This resilience allows the company to maintain its superior performance for an extended duration, resisting the erosion of its market position.
Core Components of a Sustainable Competitive Advantage
The foundation of a sustainable competitive advantage rests on several key pillars. These include possessing valuable and rare resources, establishing strong brand recognition and customer loyalty, developing unique capabilities and competencies, and fostering a culture of innovation. A company that excels in these areas is significantly better positioned to fend off competitive pressures. For instance, a strong brand reputation can command premium pricing, while unique operational processes can translate into significant cost advantages.
Examples of Companies Achieving Competitive Advantage Through Technology
Many companies have leveraged technology to create and maintain competitive advantages. Amazon, for example, utilizes its vast technological infrastructure, including sophisticated logistics and data analytics, to offer unparalleled speed and convenience in e-commerce. This has enabled them to dominate the online retail market. Similarly, Netflix used technology to disrupt the traditional movie rental industry, offering on-demand streaming and personalized recommendations, creating a superior customer experience.
Apple’s success is also largely attributed to its mastery of design, user experience, and integrated ecosystems, creating a powerful brand loyalty and a premium pricing model.
Short-Term versus Long-Term Competitive Advantage
The distinction between short-term and long-term competitive advantages lies primarily in their durability. Short-term advantages, often based on temporary market trends, promotions, or cost reductions, are easily replicated by competitors. They may provide a temporary boost in profitability but lack the staying power to create sustained market leadership. Conversely, long-term competitive advantages are built on more fundamental aspects, such as strong intellectual property, unique technological capabilities, or deeply ingrained customer loyalty.
These advantages are more difficult to replicate, providing a more resilient foundation for sustained success. For example, a company launching a new product with a cutting-edge feature might enjoy a short-term advantage until competitors develop similar offerings. However, a company with a patented technology that forms the basis of its products has a much more substantial, long-term competitive advantage.
Technology’s Role in Operational Efficiency
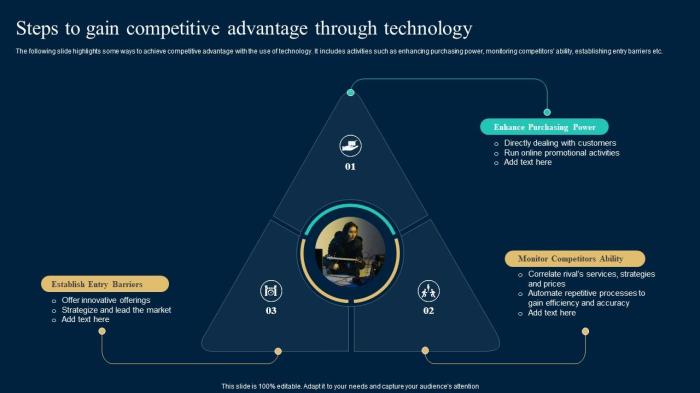
Technology plays a pivotal role in enhancing operational efficiency and reducing costs across various industries. By automating tasks, streamlining processes, and optimizing resource allocation, businesses can achieve significant improvements in productivity and profitability. This section will explore how technology contributes to operational efficiency, focusing on automation and supply chain management.
Automation Improves Operational Efficiency and Reduces Costs
Automation, driven by technological advancements like robotics, AI, and machine learning, significantly improves operational efficiency by reducing human error, increasing speed, and optimizing resource utilization. Repetitive tasks, previously handled manually, can be automated, freeing up human workers for more complex and strategic roles. This leads to a reduction in labor costs and an increase in output. For example, automated assembly lines in manufacturing drastically reduce production time and defects compared to manual processes.
Similarly, automated customer service systems, using chatbots and AI-powered virtual assistants, can handle a large volume of inquiries simultaneously, improving response times and customer satisfaction while reducing the need for a large customer service team. The cost savings are realized through decreased labor costs, reduced waste, and improved overall productivity.
Technologies that Streamline Supply Chain Management
Effective supply chain management is crucial for a company’s competitiveness. Technology plays a vital role in streamlining this process, improving visibility, and reducing lead times. Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems integrate various aspects of the supply chain, from procurement to delivery, providing a holistic view of the entire process. Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) tags provide real-time tracking of goods, improving inventory management and reducing the risk of loss or damage.
Blockchain technology offers enhanced security and transparency in supply chain transactions, building trust and accountability among stakeholders. Furthermore, sophisticated analytics platforms can analyze vast amounts of data to predict demand, optimize logistics, and proactively address potential disruptions. These technologies work together to create a more efficient, responsive, and resilient supply chain.
Comparison of Efficiency Gains from Technological Solutions
The following table compares the efficiency gains of different technological solutions, considering factors like efficiency improvement, cost, and implementation time. These values are estimates and can vary depending on specific implementation details and business contexts. For example, the implementation time for an ERP system can be significantly longer for larger companies with complex legacy systems.
| Technology | Efficiency Improvement (%) | Cost (USD) | Implementation Time (Months) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Robotics Process Automation (RPA) | 20-40 | 10,000 – 100,000 | 1-6 |
| Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) | 15-30 | 50,000 – 1,000,000+ | 6-24 |
| RFID Tracking | 10-25 | 5,000 – 50,000 | 3-12 |
| AI-powered Predictive Analytics | 15-35 | 20,000 – 200,000 | 6-18 |
Technology’s Impact on Customer Experience
In today’s competitive landscape, delivering exceptional customer experiences is paramount to success. Technology plays a crucial role in shaping these experiences, enabling businesses to engage customers more effectively, build stronger loyalty, and ultimately, gain a competitive edge. By leveraging technological advancements, companies can personalize interactions, streamline service delivery, and create a more seamless and satisfying journey for their customers.Technology significantly enhances customer engagement and loyalty by providing businesses with the tools to understand customer preferences, behaviors, and needs more deeply.
This understanding allows for targeted communication, personalized offers, and proactive service, fostering a sense of connection and appreciation that cultivates long-term loyalty. Effective use of technology fosters a more personalized and efficient customer journey, directly impacting customer satisfaction and retention rates.
Personalized Customer Experiences Through Technology
Companies are increasingly utilizing technology to personalize the customer experience at every touchpoint. For example, Amazon uses sophisticated algorithms to recommend products based on past purchases and browsing history, creating a highly individualized shopping experience. Netflix employs similar technology to suggest movies and TV shows tailored to individual viewing preferences. This level of personalization goes beyond simple recommendations; it involves creating tailored messaging, offering customized product bundles, and even adjusting website layouts to reflect individual user preferences.
Such personalized approaches significantly increase customer satisfaction and engagement.
Best Practices for Using Technology to Improve Customer Service
Effective use of technology in customer service requires a strategic approach. The following best practices highlight key considerations:
- Implement a robust CRM system: A comprehensive Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system provides a centralized repository of customer data, enabling agents to access complete customer histories and personalize interactions. This allows for more efficient and effective problem-solving, reducing resolution times and improving customer satisfaction.
- Utilize AI-powered chatbots: AI-powered chatbots can handle routine inquiries, freeing up human agents to focus on more complex issues. This improves response times and ensures 24/7 availability, enhancing customer convenience and satisfaction. Well-designed chatbots can provide immediate support, guide customers through self-service options, and escalate complex issues to human agents seamlessly.
- Offer multiple communication channels: Providing customers with a choice of communication channels, such as email, phone, live chat, and social media, caters to individual preferences and improves accessibility. This omnichannel approach ensures customers can reach support easily, regardless of their preferred method.
- Invest in comprehensive training for customer service agents: Equipping agents with the knowledge and skills to utilize technology effectively is crucial. Training should cover the use of CRM systems, AI tools, and other technologies used in customer service, ensuring seamless integration and efficient problem-solving.
- Proactively collect and analyze customer feedback: Regularly gathering and analyzing customer feedback through surveys, reviews, and social media monitoring provides valuable insights into customer satisfaction and areas for improvement. This data-driven approach allows companies to adapt and refine their customer service strategies based on real-time feedback.
Data Analytics and Competitive Intelligence
In today’s hyper-competitive business landscape, leveraging data effectively is no longer a luxury but a necessity for survival. Data analytics and competitive intelligence provide a powerful combination, offering invaluable insights that can propel a company ahead of its rivals. By systematically collecting, analyzing, and interpreting data, businesses can gain a profound understanding of market trends, customer preferences, and competitor strategies, ultimately informing strategic decision-making and driving sustainable competitive advantage.Data analytics provides insights into market trends and customer behavior by processing vast amounts of information from diverse sources.
This includes internal data like sales figures, customer service interactions, and website analytics, as well as external data such as market research reports, social media sentiment, and competitor activity. Sophisticated algorithms and statistical models are then applied to identify patterns, correlations, and anomalies, revealing valuable information about emerging trends, evolving customer needs, and potential market opportunities. For example, analyzing social media data can reveal shifts in consumer preferences, allowing companies to adapt their product offerings and marketing strategies accordingly.
Analyzing sales data can pinpoint specific product lines performing well or poorly, guiding inventory management and resource allocation.
Companies Using Data to Anticipate and Respond to Competitive Threats
Companies utilize data analytics in several ways to proactively address competitive threats. Real-time monitoring of competitor pricing, product launches, and marketing campaigns allows for rapid response and strategic adjustments. For instance, a company might use data to identify a competitor’s new marketing campaign targeting a specific demographic. This insight would allow them to tailor their own campaign to better resonate with that demographic or to develop a counter-strategy to mitigate the competitor’s impact.
Furthermore, predictive analytics can forecast potential threats, such as the emergence of disruptive technologies or shifts in consumer demand, enabling companies to develop proactive mitigation strategies. Consider a company that analyzes data indicating a growing preference for sustainable products. This would enable them to invest in research and development of eco-friendly alternatives, positioning themselves favorably before the trend becomes widespread.
Predictive Analytics and Competitive Advantage
Predictive analytics uses historical data, statistical algorithms, and machine learning techniques to forecast future outcomes. This capability offers a significant competitive advantage by allowing businesses to anticipate future trends and proactively adjust their strategies. For example, a retailer could use predictive analytics to forecast demand for specific products during peak seasons, optimizing inventory levels and minimizing stockouts or overstocking. Similarly, a financial institution might use predictive analytics to identify potential risks in its loan portfolio, allowing for early intervention and minimizing potential losses.
In the marketing domain, predictive analytics can personalize customer experiences, leading to improved conversion rates and customer loyalty. For instance, by analyzing customer purchase history and browsing behavior, a company can recommend relevant products, increasing the likelihood of a sale. The ability to accurately predict future events empowers businesses to make informed decisions, allocate resources efficiently, and gain a significant edge over competitors who rely on less sophisticated methods.
Technology and Human Capital
Technology’s impact on human capital is profound, reshaping how organizations attract, retain, and develop their workforce. It’s no longer just about efficiency; it’s about creating a dynamic and engaging work environment that fosters innovation and growth, ultimately driving a competitive advantage. This section will explore the multifaceted relationship between technology and human capital, focusing on talent acquisition, productivity enhancement, and employee development.Technology plays a crucial role in attracting and retaining top talent, significantly impacting an organization’s ability to compete effectively.
The modern job market is highly competitive, and organizations must leverage technology to stand out.
Technology’s Role in Attracting and Retaining Top Talent
Companies utilize various technological tools to attract top talent. Sophisticated Applicant Tracking Systems (ATS) streamline the recruitment process, ensuring a quicker and more efficient candidate selection. Furthermore, the use of social media platforms like LinkedIn allows for targeted recruitment campaigns, reaching potential candidates directly. Organizations also leverage employer branding strategies, often through company websites and online presence, to highlight their company culture and values, thereby attracting individuals who align with their mission.
Employee referral programs, often facilitated by internal technology platforms, encourage current employees to refer qualified candidates, leading to better hires and improved retention rates. Finally, the use of data analytics helps companies understand what attracts top talent and tailor their recruitment strategies accordingly. For example, analyzing applicant data can reveal which job postings are most effective or what skills are in highest demand.
Technology’s Enhancement of Employee Productivity and Collaboration
Technology significantly boosts employee productivity and collaboration. Cloud-based platforms enable seamless document sharing and collaborative work, eliminating the need for cumbersome email chains and version control issues. Project management software helps teams track progress, assign tasks, and manage deadlines effectively. Communication tools such as instant messaging and video conferencing facilitate real-time communication, breaking down geographical barriers and fostering a more connected workforce.
Furthermore, automation of repetitive tasks through Robotic Process Automation (RPA) frees up employees to focus on higher-value activities, increasing overall productivity. For instance, a company might use RPA to automate data entry tasks, allowing employees to focus on more strategic initiatives.
Technology’s Impact on Employee Training and Development
Different technologies offer varying impacts on employee training and development. Traditional methods, such as instructor-led training, are still relevant, but online learning platforms, including Learning Management Systems (LMS), offer scalability and flexibility. LMS platforms allow employees to access training materials at their own pace and convenience, catering to diverse learning styles. Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) technologies offer immersive training experiences, particularly beneficial for hands-on training in fields like manufacturing or healthcare.
For example, a medical student could practice surgical procedures in a VR environment before performing them on a patient. Microlearning, which involves delivering short, focused learning modules, is another effective approach facilitated by technology, promoting knowledge retention and efficient skill development. The choice of technology depends on the specific training needs, budget, and learning objectives. Companies are increasingly adopting blended learning approaches, combining online and in-person training to maximize effectiveness.
Managing Technological Risk
Embracing new technologies offers significant competitive advantages, but it also introduces a range of potential risks. A comprehensive understanding and proactive management of these risks are crucial for sustained success. Ignoring these risks can lead to financial losses, reputational damage, and even business failure. Therefore, a robust risk management framework is essential for any organization looking to leverage technology effectively.The adoption of new technologies inherently presents various challenges.
These range from the immediate costs of implementation and integration to the long-term implications of data security and system vulnerabilities. Understanding these potential pitfalls and implementing effective mitigation strategies is key to maximizing the benefits while minimizing the downsides of technological advancement. This involves careful planning, rigorous testing, and ongoing monitoring of systems and processes.
Potential Risks Associated with Technology Adoption
Organizations face a multitude of risks when adopting new technologies. These include financial risks such as unexpected costs associated with implementation, integration, and maintenance; operational risks such as system downtime, data breaches, and loss of productivity; and reputational risks such as damage to brand image due to security breaches or service failures. For example, a poorly implemented cloud migration could lead to significant downtime, resulting in lost revenue and customer dissatisfaction.
Similarly, a failure to adequately secure sensitive data could result in substantial fines and legal action.
Strategies for Mitigating Technological Risks and Ensuring Data Security
Effective risk mitigation involves a multi-pronged approach. This includes conducting thorough risk assessments to identify potential vulnerabilities, implementing robust security measures such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and encryption, and developing comprehensive disaster recovery and business continuity plans. Regular security audits and penetration testing can identify and address weaknesses before they are exploited. Furthermore, employee training on cybersecurity best practices is vital to prevent human error, a major cause of many security breaches.
For instance, implementing multi-factor authentication can significantly reduce the risk of unauthorized access. Regular data backups and a robust disaster recovery plan can minimize the impact of data loss due to hardware failure or cyberattacks.
Best Practices for Managing Risks Associated with Technology Investments
A structured approach to managing technological risks is essential. This involves establishing clear goals and objectives for technology investments, conducting thorough due diligence before making any major purchases, and developing a comprehensive risk management plan. This plan should include strategies for identifying, assessing, mitigating, and monitoring risks throughout the technology lifecycle. Regular reviews and updates to the risk management plan are necessary to adapt to evolving threats and vulnerabilities.
Furthermore, fostering a culture of security awareness within the organization is crucial. This involves educating employees about security risks and providing them with the tools and training they need to protect sensitive information. A well-defined incident response plan is also vital to ensure a swift and effective response to any security breaches.
Future Trends and Technological Disruption

The rapid pace of technological advancement is fundamentally reshaping competitive landscapes across all industries. Understanding emerging technologies and their potential disruptive impact is crucial for businesses seeking to maintain or gain a competitive edge. This section will explore several key trends and their implications for competitive advantage.The convergence of several technological advancements is creating a perfect storm of disruption.
Businesses that fail to adapt risk becoming obsolete. This necessitates proactive strategies focused on innovation, agility, and a forward-looking approach to technology adoption.
Emerging Technologies and Their Impact on Competitive Advantage
Several emerging technologies are poised to significantly alter the competitive landscape. These technologies offer opportunities for increased efficiency, enhanced customer experiences, and the development of entirely new business models. Their successful integration requires careful planning and strategic implementation.
Potential Disruptive Technologies and Their Implications for Various Industries
Artificial intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT), blockchain technology, and quantum computing are just a few examples of technologies with the potential to disrupt established industries. AI, for instance, is automating tasks, improving decision-making, and personalizing customer experiences across sectors like manufacturing, finance, and healthcare. The IoT is creating new data streams and opportunities for optimization in areas such as supply chain management and smart cities.
Blockchain technology offers potential for increased transparency and security in transactions, impacting industries like finance and logistics. Quantum computing, while still in its early stages, promises to revolutionize fields requiring complex computations, such as drug discovery and materials science. The implications of these technologies are far-reaching and will vary depending on the specific industry and the ability of companies to adapt and innovate.
For example, the rise of e-commerce has dramatically reshaped the retail industry, forcing traditional brick-and-mortar stores to adapt or face decline.
The Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Competitive Landscapes
Artificial intelligence is rapidly transforming competitive landscapes across various sectors. AI-powered systems are enhancing operational efficiency through automation, predictive maintenance, and optimized resource allocation. In customer service, AI-driven chatbots and personalized recommendations are improving customer experiences and loyalty. Moreover, AI is enabling the development of new products and services, creating entirely new market opportunities. For instance, AI-powered diagnostic tools are revolutionizing healthcare, while AI-driven algorithms are optimizing financial trading strategies.
However, the successful implementation of AI requires significant investment in infrastructure, data, and skilled personnel. Companies must also address ethical considerations and potential biases associated with AI algorithms. The competitive advantage will accrue to those organizations that effectively leverage AI to improve efficiency, enhance customer experiences, and develop innovative products and services, while mitigating potential risks. Consider, for example, the use of AI in fraud detection by financial institutions, significantly reducing losses and improving security.
This represents a clear competitive advantage gained through AI adoption.
Ultimately, the role of technology in achieving competitive advantage extends far beyond simple automation or efficiency gains. It’s about fostering a culture of innovation, data-driven decision-making, and customer-centricity. Successfully integrating technology across all aspects of the business—from product development to customer service—creates a synergistic effect, leading to a stronger brand, higher profitability, and lasting market dominance. The companies that master this integration will be the ones best positioned for future success in an increasingly digital world.
FAQ Insights
What are some common technology pitfalls to avoid when striving for competitive advantage?
Overspending on technology without a clear strategy, neglecting cybersecurity, failing to adapt to changing technological landscapes, and insufficient employee training are all significant risks.
How can small businesses leverage technology to compete with larger corporations?
Small businesses can leverage cloud-based solutions for scalability, utilize agile methodologies for rapid development, focus on niche markets, and build strong online presences to compete effectively.
What is the importance of ethical considerations in technology adoption for competitive advantage?
Ethical considerations are paramount. Using data responsibly, protecting customer privacy, and ensuring fair and unbiased algorithmic decision-making are crucial for maintaining trust and long-term sustainability.