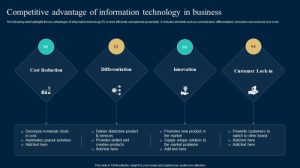
In today’s dynamic business landscape, securing a sustainable competitive advantage is paramount for long-term success. This exploration delves into the multifaceted strategies and approaches necessary to not only identify but also cultivate and maintain a distinct edge over competitors. We’ll examine the core components of a robust competitive advantage, exploring diverse avenues such as innovation, operational excellence, and strategic positioning within the market.
From understanding the competitive landscape and leveraging resources effectively to adapting to evolving market dynamics and fostering unwavering customer loyalty, we’ll navigate the key principles that underpin the creation and preservation of a truly competitive advantage. Real-world case studies will illuminate successful strategies and highlight the critical elements required for sustained dominance in any industry.
Defining Competitive Advantage
A competitive advantage is what sets a business apart from its rivals, allowing it to outperform them and capture a larger market share. It’s not simply about being better; it’s about possessing something uniquely valuable that customers are willing to pay a premium for, or that allows the business to operate more efficiently than its competitors. This advantage must be sustainable over time to truly impact long-term success.A sustainable competitive advantage rests on several core components.
Firstly, it must be valuable, providing tangible benefits to customers or the business itself. Secondly, it needs to be rare, meaning few competitors possess it. Thirdly, it must be inimitable, difficult or costly for others to replicate. Finally, it needs to be non-substitutable, meaning there aren’t readily available alternatives that offer similar value. Only when all these elements are present can a competitive advantage be considered truly sustainable.
Examples of Businesses with Strong Competitive Advantages
Apple, for example, has cultivated a strong competitive advantage built on a combination of factors. Their brand recognition is unparalleled, creating significant customer loyalty. Their ecosystem of interconnected products and services creates a high switching cost for consumers. Furthermore, their design-centric approach consistently delivers innovative and desirable products. These elements, combined, create a powerful and enduring competitive advantage.
Similarly, Amazon’s dominance in e-commerce stems from its vast logistics network, its powerful recommendation engine, and its Prime membership program, all of which are difficult for competitors to fully replicate.
Approaches to Identifying Potential Competitive Advantages
Identifying a potential competitive advantage requires a strategic approach. One approach involves analyzing the value chain, identifying specific activities where the business can create superior value compared to its competitors. This might involve streamlining operations to reduce costs, developing unique product features, or creating a superior customer experience. Another approach focuses on analyzing market needs and gaps, identifying unmet customer needs or underserved market segments.
By focusing on these underserved areas, a business can develop a unique offering that resonates with a specific customer base, creating a niche competitive advantage. A third approach involves leveraging internal resources and capabilities. This involves assessing the company’s unique strengths, such as proprietary technology, skilled workforce, or strong brand reputation, and determining how these can be leveraged to create a competitive edge.
Sources of Competitive Advantage
Creating a sustainable competitive advantage requires a deep understanding of the various factors that contribute to a company’s success in the marketplace. These sources are interconnected and often reinforce each other, leading to a powerful and enduring position. This section will explore key sources, examining their individual contributions and their synergistic effects.
Innovation as a Source of Competitive Advantage
Innovation, the process of creating something new and valuable, is a powerful driver of competitive advantage. It can manifest in various forms, from developing entirely new products and services to significantly improving existing ones. Disruptive innovations, in particular, can reshape entire industries by creating new markets and rendering existing ones obsolete. These innovations often start by targeting niche markets before expanding to disrupt the mainstream.Disruptive innovations often challenge established players by offering simpler, more affordable, or more accessible solutions.
Consider the impact of digital photography on the film industry. Digital cameras, initially inferior in image quality, offered convenience and affordability, gradually eroding the market share of film cameras until they became largely obsolete. Similarly, smartphones disrupted the market for dedicated GPS devices, music players, and even traditional cameras. Netflix’s streaming service disrupted the traditional video rental market, demonstrating the power of a disruptive business model.
Operational Excellence as a Source of Competitive Advantage
Operational excellence focuses on streamlining processes, improving efficiency, and reducing costs throughout the value chain. Companies that achieve operational excellence consistently deliver high-quality products or services at competitive prices, leading to improved profitability and customer satisfaction. This often involves the implementation of lean manufacturing principles, advanced technologies, and effective supply chain management.
Process Flow Diagram for Efficient Operations (Illustrative Example):
Imagine a simplified process for online order fulfillment. The flow would look like this:
1. Order Placement: Customer places order via website.
2. Order Verification: System verifies order details and payment.
3. Inventory Check: System checks inventory availability.
4. Order Fulfillment: Warehouse staff picks and packs the order.
5. Shipping: Order is shipped to the customer via chosen carrier.
6. Delivery Confirmation: Customer receives delivery confirmation.
7. Post-Delivery Feedback: Customer is invited to provide feedback.
Efficient operations are characterized by minimal bottlenecks, clear communication, and effective use of technology at each stage. This diagram, while simplified, highlights the importance of a streamlined and well-defined process flow.
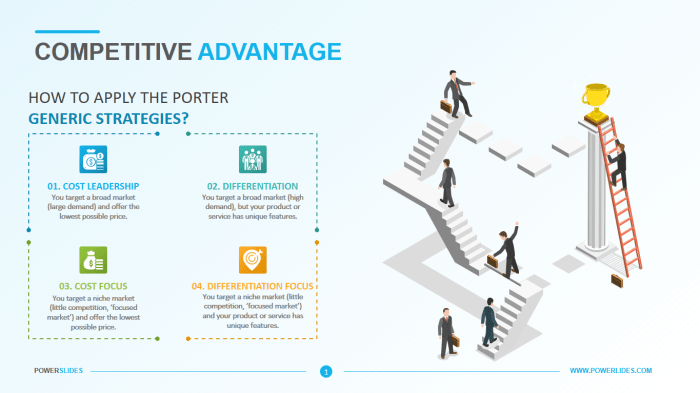
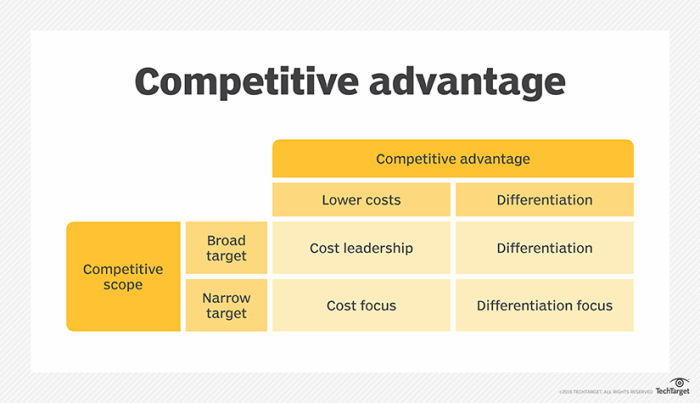
Cost Leadership versus Differentiation
Cost leadership and differentiation are two fundamental competitive strategies. Cost leadership focuses on achieving the lowest cost of production and distribution, allowing companies to offer the most competitive prices. Differentiation, on the other hand, focuses on creating unique and valuable products or services that command a premium price. Each strategy has its own strengths and weaknesses.
| Company | Strategy | Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|---|
| Walmart | Cost Leadership | High volume, low prices, strong market share | Lower profit margins, vulnerability to price wars |
| Apple | Differentiation | Premium pricing, strong brand loyalty, high profit margins | Higher production costs, vulnerability to imitation |
| Southwest Airlines | Cost Leadership (with elements of differentiation – customer service) | Low fares, high efficiency, broad appeal | Limited amenities, potential for service cuts to reduce costs |
| Mercedes-Benz | Differentiation | Luxury branding, high quality, strong brand image | Higher prices, limited market reach |
Analyzing the Competitive Landscape
Understanding the competitive landscape is crucial for developing a sustainable competitive advantage. A thorough analysis allows businesses to identify opportunities, anticipate threats, and strategically position themselves for success. This involves identifying key players, understanding their strategies, and assessing the overall intensity of competition within the market.
Competitive Matrix
A competitive matrix provides a visual representation of the key players in an industry and their competitive strategies. This tool facilitates a comparative analysis, highlighting each competitor’s strengths and weaknesses, market share, and strategic focus. For example, a competitive matrix for the fast-food industry might include McDonald’s, Burger King, Subway, and Wendy’s, comparing them based on factors like menu offerings, pricing strategies, geographic reach, and marketing campaigns.
The matrix would visually demonstrate the relative positioning of each competitor, revealing potential areas for differentiation and competitive advantage. Constructing a robust matrix requires identifying the most relevant competitive factors within the industry and assigning weights to them based on their importance.
Factors Influencing Competitive Intensity
Several factors contribute to the intensity of competition within a specific market. These factors determine the ease or difficulty of achieving and maintaining a competitive advantage. High levels of rivalry among existing competitors, the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of suppliers and buyers, and the threat of substitute products all significantly influence competitive dynamics. For example, an industry with low barriers to entry, like food trucks, will typically experience higher competitive intensity than one with high barriers, such as pharmaceutical manufacturing.
Similarly, an industry with powerful buyers, such as the retail sector, will face intense pressure on pricing and margins.
Porter’s Five Forces
Porter’s Five Forces model provides a framework for analyzing the competitive intensity and attractiveness of an industry. These forces are: the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of suppliers, the bargaining power of buyers, the threat of substitute products or services, and the rivalry among existing competitors. Each force exerts a different level of pressure on profitability and shapes the competitive landscape.
For instance, a high threat of new entrants indicates a less attractive industry, as new competitors can easily erode market share and reduce profitability. Conversely, a strong bargaining power of suppliers can lead to increased input costs, squeezing profit margins. Understanding the interplay of these five forces is critical for identifying opportunities to develop and sustain a competitive advantage.
A company operating in an industry with weak forces will find it easier to build and maintain a competitive advantage compared to a company in an industry characterized by strong forces.
Building a Competitive Advantage
Building a sustainable competitive advantage requires a proactive and strategic approach. It’s not simply about being better than the competition; it’s about creating something unique and difficult to replicate, allowing your business to thrive in the long term. This involves a deep understanding of your market, your resources, and the potential for innovation.
This section details the crucial steps involved in constructing a powerful competitive advantage, from designing a unique selling proposition to leveraging resources and safeguarding intellectual property.
Strategic Planning for a Unique Selling Proposition
Developing a unique selling proposition (USP) is paramount. A USP is a clear statement that differentiates your product or service from the competition, highlighting its unique value to customers. It should be concise, memorable, and resonate with your target audience. The process involves thorough market research to identify unmet needs or underserved segments, analyzing competitor offerings to identify gaps, and then crafting a value proposition that speaks directly to those needs and gaps.
For example, a company might focus on superior customer service as its USP, offering 24/7 support and personalized attention that competitors lack. Alternatively, a company might emphasize sustainability and ethical sourcing as its USP, attracting environmentally conscious consumers. A well-defined USP forms the foundation for all subsequent marketing and business strategies.
Leveraging Resources and Capabilities for Competitive Advantage
A company’s resources and capabilities are the building blocks of its competitive advantage. Resources include tangible assets like equipment and technology, as well as intangible assets like brand reputation and intellectual property. Capabilities refer to the organization’s ability to effectively utilize these resources. For example, a company with advanced manufacturing technology (resource) and a highly skilled workforce capable of efficiently operating that technology (capability) can achieve a significant cost advantage over competitors.
Similarly, a company with a strong brand reputation (resource) and the marketing expertise to leverage that reputation (capability) can command premium prices. Identifying and strategically deploying core competencies—unique capabilities that are difficult for competitors to imitate—is crucial for sustainable competitive advantage. This often involves investing in research and development, employee training, and process optimization.
The Importance of Intellectual Property in Protecting a Competitive Advantage
Intellectual property (IP) protection is critical for safeguarding a competitive advantage. IP encompasses patents, trademarks, copyrights, and trade secrets, all of which can provide a significant barrier to entry for competitors. Patents protect inventions, giving the patent holder exclusive rights to manufacture, use, and sell the invention for a specified period. Trademarks protect brand names and logos, ensuring brand recognition and preventing confusion in the marketplace.
Copyrights protect original works of authorship, such as software code, designs, and marketing materials. Trade secrets, such as unique formulas or processes, can offer significant competitive advantages if kept confidential. A strong IP portfolio can significantly enhance a company’s market position and defend against imitation. For instance, pharmaceutical companies rely heavily on patent protection for their new drug discoveries, preventing competitors from producing generic versions for a specific period.
Similarly, technology companies often use patents and copyrights to protect their software and hardware innovations.
Maintaining a Competitive Advantage
Sustaining a competitive advantage requires more than just establishing one; it demands constant vigilance and proactive adaptation. The business landscape is dynamic, with evolving consumer preferences, technological advancements, and shifting economic conditions constantly reshaping the competitive playing field. Successfully navigating this requires a multi-faceted approach that prioritizes flexibility, innovation, and customer centricity.Adapting to Changing Market Conditions and Maintaining a Competitive Edge involves a proactive approach to market analysis and strategic responsiveness.
This isn’t simply reacting to changes, but anticipating them and positioning the business to capitalize on opportunities and mitigate threats. This requires robust market research, a flexible organizational structure capable of quick pivots, and a willingness to embrace change.
Strategies for Adapting to Market Change
Effective adaptation hinges on several key strategies. Regular market research helps identify emerging trends and shifts in consumer demand. This allows businesses to proactively adjust their product offerings, marketing strategies, and operational processes to remain relevant and competitive. Furthermore, fostering a culture of innovation within the organization is crucial. This involves encouraging experimentation, embracing new technologies, and empowering employees to contribute creative solutions.
Finally, building strong relationships with suppliers and partners provides a crucial buffer against external shocks and ensures access to essential resources. A company that can swiftly adapt its supply chain to accommodate disruptions will have a distinct advantage over those that are less agile.
The Role of Continuous Improvement in Sustaining Competitive Advantage
Continuous improvement, often embodied by methodologies like Kaizen or Six Sigma, is fundamental to long-term competitiveness. It’s not about making incremental changes; it’s about a commitment to ongoing optimization across all aspects of the business. This includes streamlining processes to improve efficiency, enhancing product quality to exceed customer expectations, and fostering a culture of learning and development within the organization.
For example, a manufacturing company might implement lean manufacturing principles to reduce waste and improve productivity, while a software company might adopt agile development methods to enhance responsiveness to customer feedback and market demands. This constant pursuit of excellence ensures that the company remains at the forefront of its industry, consistently delivering superior value to its customers.
The Importance of Customer Loyalty in Maintaining a Long-Term Competitive Position
Customer loyalty represents a significant competitive advantage. Loyal customers are more likely to make repeat purchases, provide positive word-of-mouth referrals, and exhibit greater tolerance during periods of challenge. Building and maintaining this loyalty requires a commitment to exceptional customer service, personalized experiences, and building strong, lasting relationships. Companies like Amazon, known for its convenient delivery and customer-centric return policies, and Apple, renowned for its premium products and dedicated customer support, have cultivated exceptionally strong customer loyalty, creating significant barriers to entry for competitors.
These companies demonstrate the long-term value of prioritizing customer satisfaction and building lasting relationships.
Competitive Advantage Case Studies

This section examines real-world examples of companies that have successfully built and maintained competitive advantages, highlighting diverse strategies and the challenges faced. We will analyze both successful and less successful approaches to illustrate the complexities involved in achieving and sustaining a competitive edge in the marketplace.
Apple’s Innovation-Driven Competitive Advantage
Apple’s sustained success stems largely from its ability to consistently innovate and create products that seamlessly integrate hardware, software, and services. This integrated approach creates a powerful ecosystem that fosters brand loyalty and makes switching to competitors difficult. Their focus on user experience, design aesthetics, and a carefully curated brand image has allowed them to command premium pricing and maintain high profit margins.
This strategy contrasts sharply with companies that focus solely on cost reduction or incremental improvements. Apple’s consistent investment in R&D, coupled with its ability to anticipate and shape market trends, has been crucial to its competitive advantage. Their innovative products, like the iPhone and iPad, redefined entire industries and created entirely new markets, effectively neutralizing potential competitors by establishing a significant first-mover advantage.
Furthermore, their tightly controlled ecosystem, encompassing the App Store and other services, reinforces user dependence and generates recurring revenue streams, solidifying their position.
Comparative Analysis: Coca-Cola and PepsiCo
Coca-Cola and PepsiCo, two giants in the beverage industry, employ different competitive strategies despite operating in the same market.
The key differences between their strategies are:
- Branding and Marketing: Coca-Cola has historically focused on building a strong, emotionally resonant brand identity, emphasizing nostalgia and global recognition. PepsiCo, in contrast, has often employed more aggressive marketing tactics, targeting younger demographics and leveraging celebrity endorsements to create a more contemporary and trend-driven image.
- Product Diversification: Coca-Cola’s portfolio is heavily weighted towards its flagship Coca-Cola brand and related beverages. PepsiCo has a more diversified portfolio, including snacks (Frito-Lay) and other beverage brands (Gatorade, Quaker Oats), offering greater resilience against fluctuations in specific product categories.
- Global Market Strategy: Both companies operate globally, but their approaches differ. Coca-Cola has a strong presence in emerging markets, often adapting its products and marketing to local tastes. PepsiCo has also achieved global success, but with a potentially more pronounced focus on developed markets.
- Pricing and Distribution: Both companies utilize extensive distribution networks, but their pricing strategies vary. Coca-Cola often maintains a premium pricing strategy, leveraging its strong brand equity. PepsiCo, at times, adopts more competitive pricing strategies, particularly in price-sensitive markets.
While both companies have enjoyed significant success, their differing strategies highlight the diverse paths to competitive advantage within a single industry. Coca-Cola’s focus on brand building has created exceptional brand loyalty, while PepsiCo’s diversification has offered greater stability and resilience to market changes.
Overcoming Competitive Threats: Netflix’s Strategic Response
Netflix faced significant competitive threats from the emergence of new streaming services like Disney+, HBO Max, and others. To maintain its market position, Netflix employed several strategies:
Netflix’s key responses to competitive threats included:
- Content Diversification: Netflix expanded its content library beyond licensed programming, investing heavily in original series and films to create exclusive content that differentiates it from competitors.
- Improved User Experience: Continuous improvements to its platform, including enhanced recommendation algorithms and personalized features, aimed to retain subscribers and attract new ones.
- Global Expansion: Netflix continued its global expansion, tapping into new markets and subscriber bases to offset potential losses in existing markets.
- Price Adjustments and Tiered Plans: Netflix strategically adjusted its pricing structure, introducing tiered plans to cater to different consumer needs and budgets, thereby maintaining affordability while offering enhanced features in higher-tier plans.
By proactively adapting to the changing competitive landscape, Netflix has managed to retain its position as a leading streaming service, demonstrating the importance of flexibility and strategic response in maintaining a competitive advantage.
Ultimately, building a lasting competitive advantage requires a strategic blend of innovation, operational efficiency, and a deep understanding of the competitive landscape. By consistently adapting to market changes, nurturing customer loyalty, and leveraging unique resources and capabilities, businesses can solidify their position and achieve sustained success. The journey demands continuous improvement and a proactive approach to identifying and capitalizing on emerging opportunities.
The reward, however, is a robust and enduring competitive edge.
Top FAQs
What is a unique selling proposition (USP)?
A USP is a statement that highlights what makes your product or service different and better than your competitors. It should be concise, memorable, and clearly communicate your value proposition.
How can I analyze my competitors effectively?
Conduct thorough market research, analyze their strengths and weaknesses, understand their pricing strategies, and identify their target markets. Utilize competitive analysis tools and frameworks.
What role does marketing play in building a competitive advantage?
Marketing is crucial for communicating your USP and value proposition to your target audience. Effective marketing helps build brand awareness, generate leads, and drive sales, reinforcing your competitive advantage.
How important is intellectual property protection?
Protecting your intellectual property (patents, trademarks, copyrights) is vital to safeguard your unique innovations and prevent competitors from replicating your success.