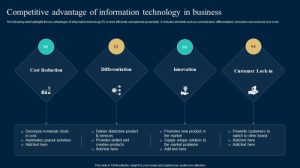
In today’s fiercely competitive business landscape, standing out from the crowd is paramount. Differentiation, the act of creating a unique value proposition that sets a company apart from its rivals, is no longer a luxury but a necessity for long-term success. This exploration delves into the multifaceted strategies involved in establishing and maintaining a competitive advantage through effective differentiation, examining both successful implementations and potential pitfalls.
We will analyze various approaches to differentiation, from product innovation and superior service to powerful branding and targeted marketing. The journey will encompass identifying unique strengths, understanding customer needs, and implementing strategies to effectively communicate a company’s distinct value proposition. Furthermore, we will explore the crucial role of innovation in sustaining a competitive edge in a constantly evolving market, and the importance of measuring success through key performance indicators.
Defining Differentiation and Competitive Advantage
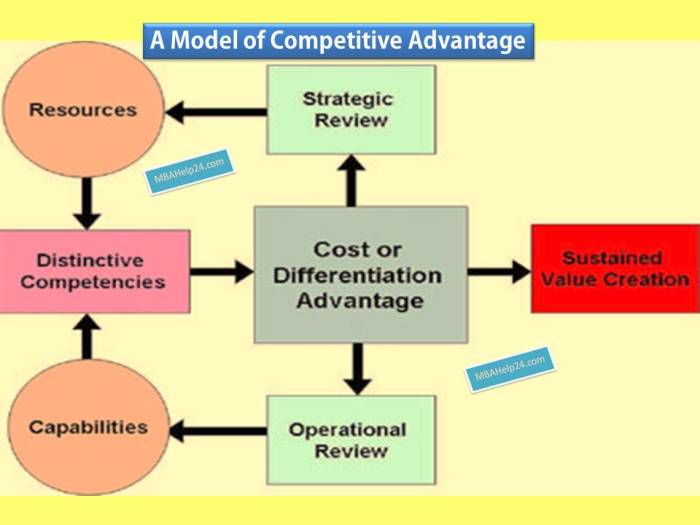
Differentiation and competitive advantage are intertwined concepts crucial for long-term business success. A competitive advantage allows a company to outperform its rivals, while differentiation is a key strategy to achieve this advantage. Essentially, differentiation involves creating a unique value proposition that sets a company apart from its competitors in the eyes of the consumer. This uniqueness can stem from various aspects of the business, from product features to customer service.
Differentiation, at its core, is about offering something distinct and valuable to customers that competitors cannot easily replicate. This uniqueness can be based on superior product quality, innovative features, exceptional customer service, strong branding, or a combination of these elements. By successfully differentiating itself, a company can command premium prices, build brand loyalty, and attract a dedicated customer base, ultimately leading to higher profitability and a sustainable competitive advantage.
Examples of Successful Differentiation Strategies
Many companies have leveraged differentiation to achieve remarkable success. Apple, for instance, has consistently differentiated itself through its sleek design, user-friendly interfaces, and strong brand image, commanding premium prices for its products. Similarly, Starbucks has built a competitive advantage through its carefully cultivated brand experience, focusing on ambiance, quality coffee, and personalized service, creating a distinct market position.
In the automotive industry, Tesla’s differentiation is based on its electric vehicle technology, advanced self-driving features, and sustainable brand image, appealing to a niche market willing to pay a premium for these features. These examples highlight the diverse ways companies can achieve differentiation.
Cost Leadership versus Differentiation
Cost leadership and differentiation represent two distinct competitive strategies. Cost leadership focuses on achieving the lowest production and distribution costs to offer the most competitive prices in the market. Companies employing this strategy often target price-sensitive consumers and compete primarily on price. Differentiation, conversely, prioritizes creating unique value propositions that justify higher prices. While cost leadership seeks to be the cheapest, differentiation aims to be the best or most desirable in a specific area.
A company can pursue a hybrid strategy, combining elements of both, but focusing purely on one typically yields better results. Choosing between these strategies depends heavily on the industry, target market, and the company’s resources and capabilities.
Comparative Analysis of Differentiation Strategies
The following table compares and contrasts various differentiation strategies:
| Differentiation Strategy | Description | Examples | Advantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Product Differentiation | Offering unique product features, superior quality, or innovative design. | Apple (innovative design and features), Tesla (electric vehicle technology) | Higher profit margins, strong brand loyalty, less price competition. |
| Service Differentiation | Providing exceptional customer service, personalized attention, or convenient access. | Starbucks (customer experience), Ritz-Carlton (luxury service) | Increased customer satisfaction, repeat business, positive word-of-mouth. |
| Brand Differentiation | Building a strong brand image, reputation, and emotional connection with customers. | Nike (athletic performance and inspiration), Coca-Cola (iconic brand recognition) | Premium pricing power, strong brand loyalty, reduced price sensitivity. |
| Distribution Differentiation | Offering convenient access to products through multiple channels or strategic locations. | Amazon (extensive online retail network), Walmart (wide store network) | Increased market reach, customer convenience, competitive advantage in accessibility. |
Identifying Sources of Differentiation
Differentiation, the process of setting your business apart from competitors, hinges on identifying and leveraging unique value propositions. This involves a deep understanding of your company’s strengths and weaknesses, a thorough assessment of the competitive landscape, and a keen awareness of customer needs and preferences. Effectively identifying these sources is critical for establishing a sustainable competitive advantage.Understanding how a unique value proposition contributes to differentiation is paramount.
A unique value proposition clearly articulates the specific benefits a company offers that are distinct from its rivals. It answers the crucial question: “Why should a customer choose us over the competition?” This proposition isn’t merely a list of features; it’s a compelling statement that resonates with the target audience and highlights the unique value derived from the product or service.
For example, a software company might offer a unique value proposition centered around unparalleled ease of use, leading to significant time savings for its customers. This clear articulation of value directly translates into differentiation.
Identifying Unique Strengths and Weaknesses
A comprehensive SWOT analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats) is a fundamental tool for identifying a company’s unique capabilities and vulnerabilities relative to its competitors. This involves meticulously examining internal factors (strengths and weaknesses) such as technological expertise, brand reputation, financial resources, and operational efficiency. Simultaneously, it necessitates an equally thorough assessment of external factors (opportunities and threats) including market trends, competitive actions, regulatory changes, and technological advancements.
By comparing the company’s profile to that of its main competitors, a clear picture emerges of its relative advantages and disadvantages. For instance, a smaller technology firm might find its strength in agility and innovation, while a larger competitor might possess a wider distribution network and brand recognition as its strengths. Understanding these disparities is crucial for shaping a successful differentiation strategy.
The Role of Market Research in Differentiation
Market research plays a pivotal role in guiding differentiation strategies. It provides invaluable insights into customer needs, preferences, and pain points. Through techniques such as surveys, focus groups, and competitive analysis, companies can gather data to identify unmet needs or areas where existing solutions fall short. This information informs the development of unique product features, targeted marketing campaigns, and customized service offerings.
For example, market research might reveal a strong customer preference for sustainable and ethically sourced products, prompting a technology company to focus on developing environmentally friendly solutions and highlighting this aspect in its marketing materials. Without this understanding, differentiation efforts risk being misaligned with actual customer demands, rendering them ineffective.
Potential Sources of Differentiation in the Technology Sector
Understanding the various potential avenues for differentiation is critical for any technology company. Below are five potential sources:
- Superior Technology: Offering cutting-edge technology that significantly outperforms competitors in terms of speed, efficiency, or functionality. This could involve proprietary algorithms, innovative hardware, or unique software integrations.
- Exceptional Customer Service: Providing unparalleled customer support and responsiveness, exceeding customer expectations and building strong brand loyalty.
- Strong Brand Reputation: Cultivating a trusted and well-respected brand image through consistent quality, ethical practices, and positive customer experiences.
- Niche Market Focus: Specializing in a specific segment of the market with unique needs and preferences, allowing for deep expertise and tailored solutions.
- Innovative Business Model: Employing a novel business model, such as subscription services or freemium offerings, that offers a distinct value proposition to customers.
Implementing a Differentiation Strategy
Successfully implementing a differentiation strategy requires a methodical approach, moving beyond simply identifying unique selling points to actively embedding them into every facet of the business. This involves not only product development and marketing but also operational efficiency and internal culture. A strong differentiation strategy requires a clear understanding of the target market and a commitment to delivering exceptional value.
Developing and implementing a differentiation strategy involves a multi-stage process that integrates various business functions. It’s not a one-time project but an ongoing process of refinement and adaptation in response to market changes and competitor actions. This iterative approach ensures the company remains relevant and competitive.
Steps in Developing and Implementing a Differentiation Strategy
The process of building and executing a differentiation strategy can be broken down into key sequential steps. Each step builds upon the previous one, creating a robust and sustainable competitive advantage.
- Define the Target Market: Thoroughly research and understand the needs, preferences, and pain points of your ideal customer. This detailed understanding forms the foundation for crafting a compelling value proposition.
- Identify Key Differentiators: Based on market research, pinpoint what makes your offering unique and superior to competitors. This could be superior quality, innovative features, exceptional customer service, or a strong brand identity.
- Develop a Value Proposition: Articulate clearly how your unique differentiators address the target market’s needs and deliver superior value. This value proposition should be concise, memorable, and easily understood.
- Develop the Product/Service: Design and develop your product or service to reflect the defined value proposition. This involves careful consideration of design, functionality, quality, and other relevant factors.
- Develop a Marketing and Communication Plan: Craft a marketing strategy that effectively communicates your unique value proposition to the target market. This might involve targeted advertising, content marketing, public relations, and social media engagement.
- Monitor and Adapt: Continuously monitor market trends, competitor actions, and customer feedback to identify areas for improvement and adaptation of the differentiation strategy. Flexibility is crucial for long-term success.
Examples of Successful Differentiation Marketing Campaigns
Several companies have successfully leveraged differentiation in their marketing campaigns, resulting in increased brand loyalty and market share. These examples highlight the power of effectively communicating a unique value proposition.
- Apple: Apple consistently differentiates itself through design, user experience, and a strong brand ecosystem. Their marketing campaigns focus on simplicity, elegance, and seamless integration across devices, resonating with a tech-savvy audience.
- Tesla: Tesla’s differentiation lies in its focus on electric vehicles, sustainability, and advanced technology. Their marketing highlights the performance, environmental benefits, and cutting-edge features of their cars, attracting environmentally conscious and tech-enthusiast buyers.
- Dove: Dove’s marketing campaigns differentiate the brand through its focus on real beauty and body positivity. By showcasing diverse body types and promoting self-acceptance, Dove has built a strong brand identity and loyal customer base.
Communicating a Company’s Unique Value Proposition
Effectively communicating a company’s unique value proposition is critical for success. This requires a clear and consistent message delivered through multiple channels. Understanding the target audience’s communication preferences is key.
This involves using targeted messaging across different channels. For example, a B2B company might utilize LinkedIn and industry publications, while a B2C company might leverage social media, influencer marketing, and traditional advertising. Consistent branding and messaging across all channels are essential for reinforcing the company’s unique identity and value proposition.
Launching a Differentiated Product or Service: A Step-by-Step Guide
Launching a differentiated product or service requires a well-defined plan. The following steps Artikel the key stages involved in bringing a differentiated offering to market successfully.
- Market Research and Analysis: Conduct thorough market research to identify opportunities and validate the uniqueness of your offering.
- Product Development and Design: Develop a product or service that embodies your unique value proposition, paying close attention to quality and functionality.
- Branding and Messaging: Develop a strong brand identity and clear messaging that effectively communicates your unique value proposition to your target audience.
- Marketing and Sales Strategy: Develop a comprehensive marketing and sales strategy to reach your target market and generate leads.
- Launch and Promotion: Launch your product or service with a well-planned marketing campaign that generates excitement and awareness.
- Post-Launch Monitoring and Analysis: Monitor performance, gather customer feedback, and make adjustments as needed to optimize your strategy.
Sustaining a Competitive Advantage through Differentiation

Maintaining a differentiated position requires ongoing effort and adaptation. The dynamic nature of modern markets means that even the most successful differentiation strategies can erode over time if not actively managed and evolved. Competitors constantly seek ways to imitate or surpass established advantages, while consumer preferences and technological advancements shift the competitive landscape.
Challenges of Maintaining Differentiation in Dynamic Markets
Sustaining a differentiated position presents several key challenges. Firstly, imitation by competitors is a constant threat. Competitors may try to replicate unique features, services, or brand experiences, thereby diminishing the perceived uniqueness of the differentiated offering. Secondly, changing consumer preferences can render existing differentiators obsolete. What appeals to customers today might not resonate tomorrow, necessitating a proactive approach to understanding evolving market demands.
Finally, rapid technological advancements can disrupt entire industries, rendering previous advantages irrelevant and requiring businesses to adapt swiftly to stay competitive. For example, the rise of digital streaming services significantly impacted the traditional cable television industry, requiring companies to adapt their offerings and strategies to remain relevant.
Protecting Intellectual Property and Key Differentiators
Protecting intellectual property (IP) is paramount to sustaining a differentiation strategy. This includes patents, trademarks, copyrights, and trade secrets. Robust IP protection prevents competitors from directly copying core differentiators. Beyond legal protection, maintaining secrecy around unique processes, formulas, or designs is crucial. Strong non-disclosure agreements with employees and partners help safeguard confidential information.
Continuous innovation and the development of new IP further strengthens the company’s defensible position. For example, pharmaceutical companies invest heavily in patents to protect their drug formulations and manufacturing processes, maintaining their competitive edge.
Threats to Differentiation Strategies and Mitigation Plans
Several threats can undermine a company’s differentiation strategy. Cost-cutting measures, if not carefully implemented, can compromise quality and diminish the perceived value of the differentiated offering. Poor customer service can negatively impact brand perception and erode customer loyalty, even if the product itself is unique. Finally, failure to adapt to changing market conditions, such as technological advancements or shifts in consumer preferences, can render a differentiation strategy ineffective.
Mitigation plans involve proactive monitoring of the competitive landscape, investing in customer relationship management (CRM) systems to improve service, and fostering a culture of innovation to adapt quickly to change. A strong brand reputation, built on consistent quality and positive customer experiences, serves as a robust defense against competitive pressures.
The Role of Innovation in Sustaining Competitive Advantage
Innovation is the lifeblood of sustained differentiation. Continuously improving existing products or services, developing entirely new offerings, and leveraging technological advancements are essential for staying ahead of the competition. This involves not only incremental improvements but also disruptive innovations that reshape the market. For example, Apple’s consistent innovation in smartphone technology, introducing new features and designs, has allowed them to maintain a strong competitive advantage despite numerous competitors.
Investing in research and development (R&D), fostering a culture of creativity, and embracing agile development methodologies are crucial for driving continuous innovation and sustaining a competitive advantage.
Measuring the Success of a Differentiation Strategy
A successful differentiation strategy isn’t just about creating a unique product or service; it’s about demonstrably improving key business metrics. Measuring the impact of this strategy requires a multifaceted approach, tracking not only financial performance but also customer perception and market positioning. The right metrics will provide clear insights into the effectiveness of your efforts and highlight areas needing adjustment.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) for Differentiation
Several key performance indicators (KPIs) are crucial for evaluating the success of a differentiation strategy. These metrics offer a comprehensive view of how well the chosen differentiation is resonating with the target market and contributing to the overall business objectives. They should be selected based on the specific differentiation strategy and overall business goals. Using a combination of qualitative and quantitative metrics provides the most robust assessment.
Metrics for Tracking Market Share, Customer Satisfaction, and Profitability
Market share growth directly reflects the success of the differentiation strategy in attracting customers. An increase in market share indicates that the unique value proposition is resonating with the target market. Customer satisfaction, measured through surveys, feedback forms, and Net Promoter Score (NPS), reveals how well the differentiated offering meets customer expectations. High customer satisfaction often translates to increased loyalty and positive word-of-mouth marketing.
Profitability, expressed as gross margin, return on investment (ROI), and profit margin, demonstrates the financial impact of the differentiation strategy. A successful strategy should improve profitability by commanding premium prices or reducing costs due to increased efficiency.
Methods for Analyzing the Effectiveness of a Differentiation Strategy
Analyzing the effectiveness of a differentiation strategy involves comparing performance metrics before and after the implementation of the strategy. This comparative analysis helps quantify the impact of the implemented changes. Benchmarking against competitors provides valuable insights into the relative performance of the differentiation strategy. By comparing key metrics with those of competitors, businesses can identify areas of strength and weakness.
Regression analysis can be used to isolate the effect of the differentiation strategy on specific outcomes, controlling for other factors that might influence performance. This method helps establish a causal relationship between the strategy and the observed results. Qualitative data, such as customer feedback and market research, can be used to supplement quantitative data and provide a richer understanding of the strategy’s impact.
Examples of KPIs and Measurement Methods
| KPI | Description | Measurement Method | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Market Share | Percentage of the total market controlled by the company. | Sales data, market research reports | Increased market share from 5% to 10% in the premium segment after implementing a differentiation strategy focused on superior quality. |
| Customer Satisfaction (CSAT) | Measure of how satisfied customers are with the product or service. | Customer surveys, feedback forms | CSAT score increased from 75% to 90% after introducing a personalized customer service program. |
| Net Promoter Score (NPS) | Measure of customer loyalty and willingness to recommend. | Customer surveys | NPS increased from 30 to 60 after enhancing product features based on customer feedback. |
| Gross Margin | Percentage of revenue remaining after deducting the cost of goods sold. | Financial statements | Gross margin increased from 40% to 50% due to premium pricing enabled by the unique product features. |
| Customer Lifetime Value (CLTV) | Prediction of the net profit attributed to the entire future relationship with a customer. | Customer purchase history, churn rate, average purchase value | CLTV increased by 25% due to improved customer retention rates resulting from superior product quality and customer service. |
Case Studies of Competitive Advantage
This section examines two contrasting case studies: one showcasing successful differentiation leading to a sustained competitive advantage, and another illustrating the pitfalls of ineffective differentiation resulting in market failure. Analyzing these examples highlights crucial factors contributing to success or failure in implementing a differentiation strategy.
Apple’s Success Through Differentiation
Apple’s consistent success can be largely attributed to its masterful implementation of a differentiation strategy. Rather than competing solely on price, Apple focuses on creating a unique ecosystem of aesthetically pleasing, user-friendly products and services. This includes hardware design, software integration, and a carefully curated brand image emphasizing simplicity and innovation. Their approach involves high-quality materials, intuitive interfaces, and a strong emphasis on the user experience.
A key challenge for Apple has been maintaining this premium image while expanding into new markets and product categories. For example, the launch of the Apple Watch required significant investment in research and development and careful marketing to establish it as a premium wearable device. Despite these challenges, Apple has consistently delivered strong financial results, driven by high customer loyalty and premium pricing.
The company’s success demonstrates the power of a well-executed differentiation strategy in creating a sustainable competitive advantage.
The Failure of Blackberry’s Differentiation Strategy
In contrast to Apple’s success, Blackberry’s story serves as a cautionary tale. Initially, Blackberry dominated the smartphone market by focusing on secure email and business-oriented features. This differentiation strategy was effective in the early days of smartphones, but Blackberry failed to adapt to the evolving market demands. The rise of the iPhone, with its intuitive touch screen and app ecosystem, exposed Blackberry’s limitations.
Their attempts to catch up with touchscreen devices and a more user-friendly interface proved too little, too late. Blackberry struggled to innovate quickly enough, leading to a decline in market share and ultimately, a diminished brand value. The company’s inability to adapt and evolve its differentiation strategy, coupled with a failure to effectively respond to changing consumer preferences, highlights the importance of continuous innovation and market responsiveness in sustaining a competitive advantage.
Comparison of Apple and Blackberry
Comparing Apple and Blackberry’s experiences reveals critical factors influencing the success or failure of a differentiation strategy. Apple’s success stems from its continuous innovation, strong brand building, and a deep understanding of customer needs. They proactively adapted to market changes, consistently refining their products and services to maintain their premium positioning. Blackberry, on the other hand, suffered from a lack of adaptability, failing to respond effectively to the shift in consumer preferences and technological advancements.
Their initial differentiation strategy, while successful in its time, became obsolete without sufficient innovation and a proactive response to emerging market trends. This comparison emphasizes the need for continuous innovation, responsiveness to market dynamics, and a strong brand image to sustain a competitive advantage based on differentiation.
Ultimately, achieving and sustaining a competitive advantage through differentiation requires a strategic, multifaceted approach. It demands a deep understanding of the market, a commitment to innovation, and a relentless focus on delivering exceptional value to customers. By carefully analyzing the strategies discussed, businesses can equip themselves with the knowledge and tools to not only differentiate themselves but also to build a sustainable competitive advantage that ensures long-term prosperity.
Detailed FAQs
What are some common mistakes companies make when trying to differentiate themselves?
Common mistakes include attempting to differentiate on too many factors, failing to clearly communicate the unique value proposition, underestimating the importance of consistent brand messaging, and neglecting to protect intellectual property.
How can a small business compete with larger, more established companies through differentiation?
Small businesses can leverage niche markets, focus on exceptional customer service, build strong community relationships, and utilize agile innovation to compete effectively. They can also emphasize personalized experiences and build a strong brand identity.
What role does pricing play in a differentiation strategy?
Pricing is a critical element. Premium pricing can reinforce a perception of high quality, while competitive pricing can attract a broader customer base. The key is aligning pricing with the overall value proposition.