In today’s fiercely competitive marketplace, a strong brand is no longer a luxury but a necessity. Building a compelling brand identity is paramount to achieving a sustainable competitive advantage. This exploration delves into the multifaceted strategies and techniques employed to leverage branding for market dominance, examining the crucial interplay between brand awareness, brand equity, and effective communication.
We will explore how meticulous market research, impactful storytelling, and consistent brand messaging across various channels contribute to not only attracting but also retaining customers. Furthermore, we’ll analyze key performance indicators (KPIs) used to measure the tangible impact of branding initiatives and the crucial adaptation strategies for maintaining competitive edge in a dynamic market landscape. Ultimately, this analysis will reveal how a well-crafted brand can translate into a powerful and enduring competitive advantage.
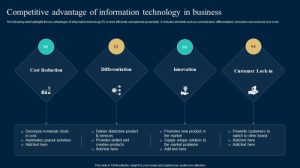
Defining Competitive Advantage Through Branding
A strong brand isn’t just a logo; it’s a powerful tool that can significantly impact a company’s market position and profitability. Competitive advantage through branding stems from creating a unique and compelling brand identity that resonates with consumers and sets a company apart from its rivals. This involves a strategic approach to building brand awareness, cultivating brand equity, and ultimately, translating these into tangible business benefits.Brand building is a multifaceted process requiring a cohesive strategy across various touchpoints.
A successful brand strategy leverages various components working synergistically to create a powerful and lasting impression.
Core Components of a Strong Brand
A strong brand is built on several key pillars. These components, when carefully integrated, contribute significantly to a company’s competitive edge, enabling it to command premium prices, attract and retain loyal customers, and withstand competitive pressures. These components include a clear and consistent brand message, a well-defined brand personality, and a strong brand identity, encompassing visual elements like logos and color palettes.
Furthermore, consistent brand experiences across all customer touchpoints are vital, ensuring that the brand promise is delivered consistently, building trust and loyalty. Finally, a robust brand story that resonates with the target audience adds emotional depth and connection.
Examples of Brands Leveraging Branding for Competitive Advantage
Several companies have masterfully utilized branding to achieve a significant competitive edge. Apple, for instance, has cultivated a premium brand image associated with innovation, design, and user experience. This perception allows them to command higher prices than competitors with comparable technology. Their minimalist aesthetic, coupled with a carefully curated brand narrative focusing on simplicity and elegance, fosters strong brand loyalty and a sense of community among its users.
Nike, another prime example, has effectively used powerful imagery and endorsements to create a brand synonymous with athletic achievement and inspiration. This association transcends mere sportswear, associating the brand with personal goals and aspirations, thus commanding significant market share. Finally, Coca-Cola’s longevity demonstrates the power of consistent brand messaging and emotional connection. Its iconic branding, coupled with a century-long commitment to a consistent brand experience, has cemented its position as a global beverage giant.
Brand Awareness versus Brand Equity in Creating Competitive Advantage
While both brand awareness and brand equity contribute to competitive advantage, they represent distinct aspects of brand strength. Brand awareness refers to the consumer’s recognition and recall of a brand. High brand awareness is essential for initial market penetration and reaching a wider audience. However, awareness alone doesn’t guarantee competitive advantage. Brand equity, on the other hand, goes beyond mere recognition.
It encompasses the overall value associated with a brand, including its reputation, customer loyalty, and perceived quality. High brand equity translates into increased customer willingness to pay a premium, reduced marketing costs due to strong customer loyalty, and a stronger resistance to competitive pressures. In essence, brand awareness lays the foundation, while brand equity builds the competitive fortress.
A brand can have high awareness but low equity, while high equity usually implies high awareness. The ultimate goal is to build both, achieving a powerful market position.
Brand Communication and Customer Experience
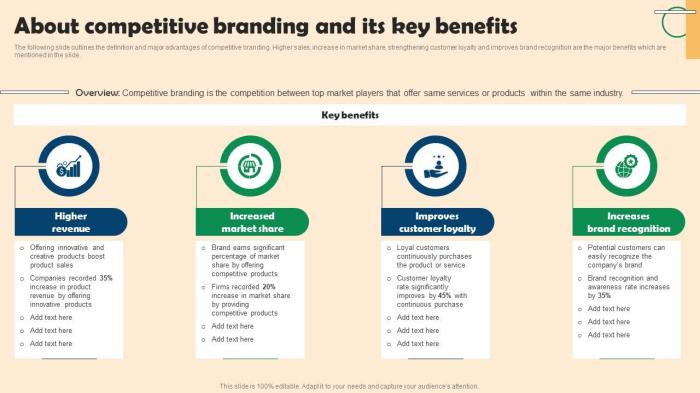
Effective brand communication and a positive customer experience are crucial for building a strong competitive advantage. A consistent brand message, delivered across all touchpoints, creates a unified and memorable brand identity, fostering trust and loyalty among consumers. Conversely, a negative customer experience can severely damage a brand’s reputation and erode its competitive edge. This section will explore how integrated communication strategies and exceptional customer service contribute to a brand’s success.
A well-executed marketing campaign can significantly enhance a brand’s competitive position by reinforcing its core values and differentiating it from competitors. Consistent messaging across various channels ensures that the brand’s personality and promises remain unified, regardless of the platform or medium. This consistency builds trust and recognition, making it easier for consumers to identify and connect with the brand.
A Marketing Campaign Demonstrating Consistent Brand Messaging
Consider a hypothetical campaign for a new sustainable clothing brand called “EcoThreads.” The core message is “Sustainable Style, Without Compromise.” This message is consistently conveyed across all channels. Their website showcases high-quality images of ethically sourced materials and production processes. Social media posts feature behind-the-scenes glimpses into the company’s ethical practices and collaborations with environmental organizations.
Print advertisements in relevant magazines highlight the durability and style of the clothing, reinforcing the “without compromise” aspect of the message. All marketing materials use a consistent color palette (earthy tones) and font, creating a unified brand identity. This cohesive messaging reinforces the brand’s commitment to sustainability and style, differentiating it from competitors who may focus solely on one or the other.
The Impact of Customer Experience on Brand Loyalty and Competitive Differentiation
Positive customer experiences directly translate to increased brand loyalty and competitive differentiation. When customers feel valued and heard, they are more likely to become repeat buyers and advocates for the brand. Conversely, negative experiences can lead to customer churn and negative word-of-mouth marketing, severely impacting a brand’s reputation and market share. Exceptional customer service, personalized interactions, and proactive issue resolution are all key elements in fostering positive customer experiences.
For example, a company known for its rapid response times and helpful customer support representatives can differentiate itself from competitors who may offer similar products but lack the same level of customer care.
Brand Communication Channels and Competitive Positioning
Brands leverage various communication channels to reach their target audiences and enhance their competitive standing. The effectiveness of each channel varies depending on the target audience and the brand’s overall marketing objectives.
| Channel | Strengths | Weaknesses | Effectiveness for Competitive Positioning |
|---|---|---|---|
| Social Media (e.g., Instagram, Facebook, TikTok) | Targeted advertising, direct customer engagement, rapid feedback, cost-effective reach | Algorithm changes, negative comments can spread quickly, requires constant monitoring and engagement | High, especially for building brand awareness and community |
| Traditional Advertising (e.g., TV, Print, Radio) | Wide reach, high brand visibility, established credibility (for some channels) | High cost, less targeted reach, difficult to measure ROI, declining viewership (for some channels) | Moderate to High, depending on the target audience and campaign execution |
| Email Marketing | Targeted messaging, high conversion rates, relatively low cost | Requires a strong email list, can be perceived as spam, high unsubscribe rates if not managed well | High, especially for nurturing leads and driving sales |
| Website/App | Direct control over brand messaging, ability to collect customer data, personalized experiences | Requires technical expertise and ongoing maintenance, needs strong for visibility | High, crucial for providing information, building trust, and driving conversions |
Measuring the Impact of Branding on Competitive Advantage

Effectively measuring the impact of branding on competitive advantage is crucial for understanding return on investment (ROI) and guiding future branding strategies. By tracking key performance indicators (KPIs) and analyzing brand perception, businesses can gain valuable insights into their brand’s health and its contribution to market success. This allows for data-driven adjustments to maintain and enhance competitive standing.Understanding the relationship between branding initiatives and business outcomes requires a multifaceted approach.
This involves selecting relevant KPIs, employing robust analytical methods to assess brand perception, and developing adaptable strategies to navigate evolving market landscapes.
Key Performance Indicators for Brand Success
Tracking specific KPIs provides quantifiable evidence of a brand’s impact. These metrics offer insights into brand awareness, customer loyalty, and ultimately, market share. Choosing the right KPIs depends on specific business goals and industry context. However, some common and valuable metrics include brand awareness (measured through surveys and social listening), customer satisfaction (through Net Promoter Score – NPS, and customer satisfaction surveys), website traffic and engagement, social media engagement, and sales revenue linked to specific branding campaigns.
A strong correlation between increased brand awareness and sales growth, for example, demonstrates the effectiveness of branding initiatives. Similarly, high NPS scores indicate strong customer loyalty, a key component of competitive advantage.
Analyzing Brand Perception and Market Share Influence
Brand perception analysis involves understanding how consumers view a brand relative to its competitors. This is achieved through various qualitative and quantitative research methods. Qualitative methods, such as focus groups and in-depth interviews, provide rich insights into consumer attitudes and opinions. Quantitative methods, like surveys and brand tracking studies, allow for the measurement of brand attributes, such as trust, quality, and innovation.
By analyzing this data, businesses can identify strengths and weaknesses in their brand positioning. For instance, a brand perceived as innovative and trustworthy might command a premium price and higher market share. Analyzing market share trends in conjunction with brand perception data helps determine the extent to which brand equity translates into market dominance. A positive correlation would suggest that a strong brand image directly contributes to increased market share.
Strategies for Adapting a Brand to Changing Market Conditions
Maintaining competitive advantage requires continuous adaptation. Market conditions are constantly evolving due to technological advancements, shifting consumer preferences, and emerging competitors. Therefore, brands must remain agile and responsive to these changes. This involves regularly monitoring market trends and consumer behavior, conducting market research to identify emerging opportunities and threats, and proactively adjusting branding strategies accordingly. For example, a brand might need to reposition itself to appeal to a younger demographic or incorporate sustainability initiatives to align with changing consumer values.
Furthermore, brands can leverage digital marketing channels to reach new audiences and personalize their messaging, enhancing engagement and loyalty. Regular brand audits, combined with ongoing market research, provide the foundation for making informed decisions about brand evolution and sustaining competitive advantage in dynamic market environments.
Competitive Advantage
Understanding competitive advantage is crucial for businesses aiming to thrive in the marketplace. A strong competitive advantage allows a company to outperform its rivals, leading to increased profitability and market share. This advantage is often built and reinforced through effective branding. This section delves into the core types of competitive advantage and examines how branding contributes to their establishment and longevity.
Types of Competitive Advantage
There are three primary types of competitive advantage: cost leadership, differentiation, and focus. Cost leadership involves offering products or services at the lowest price in the market. Differentiation focuses on offering unique and superior products or services that command a premium price. Focus strategies target specific market segments with tailored offerings. Each strategy requires a unique branding approach to effectively reach and resonate with its target audience.
Cost Leadership and Branding
Cost leadership strategies necessitate efficient operations and economies of scale. Walmart, for example, utilizes its vast distribution network and bulk purchasing power to offer consistently low prices. Their branding reinforces this value proposition through consistent messaging emphasizing affordability and everyday low prices. This clear, consistent brand message helps solidify their position as the cost leader in the retail sector.
Differentiation and Branding
Differentiation involves creating products or services that are perceived as unique and superior. Apple, a prime example, cultivates a brand image synonymous with innovation, design, and user experience. Their premium pricing is justified by the perceived value of their products and the aspirational nature of their brand. This strong brand identity allows them to command premium prices, despite the existence of functionally similar products at lower price points.
Focus and Branding
Focus strategies target niche market segments. A company like Tesla, initially, focused on the high-performance electric vehicle market. Their branding emphasizes sustainability, technology, and luxury, attracting a specific customer segment willing to pay a premium for these attributes. This targeted branding helped establish Tesla as a leader in its niche before expanding to broader market segments.
Sustainability of Competitive Advantages
Maintaining a competitive advantage over the long term is a significant challenge. A company’s ability to sustain its advantage is influenced by several factors.
- Technological advancements: Rapid technological changes can quickly render existing advantages obsolete. Companies must continuously innovate and adapt to stay ahead.
- Competitive responses: Competitors constantly strive to replicate or surpass existing advantages. Strong branding can help create barriers to entry and slow down imitation.
- Changes in customer preferences: Consumer tastes and needs are dynamic. Brands must be agile enough to adjust their offerings and messaging to remain relevant.
- Economic conditions: Macroeconomic factors like recessions or inflation can significantly impact consumer behavior and purchasing power. A resilient brand can weather these storms more effectively.
- Government regulations: Changes in regulations can impact a company’s ability to operate and maintain its competitive advantage. Adaptability and strong brand reputation are crucial in navigating regulatory changes.
Branding plays a vital role in sustaining competitive advantage by creating strong customer loyalty, building brand equity, and fostering a sense of trust and emotional connection. A strong brand acts as a shield against competitive pressures and helps ensure long-term success.
Visual Brand Elements and Competitive Advantage
Visual brand elements are far more than just aesthetically pleasing; they are fundamental building blocks of a company’s competitive identity. A well-crafted visual brand strategy leverages logo design, color palettes, and typography to create a lasting impression, fostering brand recognition and ultimately, driving competitive advantage. These elements work synergistically to communicate a brand’s personality, values, and positioning in the market, influencing consumer perception and behavior.A successful brand’s visual identity is meticulously designed to evoke specific emotions and associations.
Consider the iconic Apple logo – a simple, yet powerful, bitten apple. The clean lines and minimalist design communicate modernity and innovation. The choice of color, a sleek silver or vibrant rainbow depending on the campaign, reinforces feelings of sophistication and approachability. Similarly, the typography used across Apple’s marketing materials, characterized by its clear, modern sans-serif fonts, further emphasizes the brand’s focus on simplicity and user-friendliness.
These elements, working together, contribute to a sense of premium quality and user experience, which are crucial differentiators in the competitive tech market. The overall effect is a brand identity that resonates deeply with consumers, fostering loyalty and brand preference.
Logo Design’s Contribution to Competitive Identity
A strong logo acts as a visual shorthand for a brand, instantly communicating its essence. A well-designed logo is memorable, versatile, and adaptable across various platforms and media. It should be distinct from competitors, clearly representing the brand’s personality and values. For instance, the Nike swoosh, a simple yet powerful symbol, is instantly recognizable globally and effectively communicates movement, speed, and athleticism.
Conversely, a poorly designed logo can hinder brand recognition and dilute the brand’s message, potentially undermining its competitive position. Effective logo design requires a deep understanding of target audience, brand values, and market positioning.
Color Palettes and Their Impact on Brand Perception
Color psychology plays a significant role in brand building. Different colors evoke different emotions and associations. For example, blue often conveys trust and stability, while green suggests nature and freshness. Red can represent excitement and energy, while yellow can symbolize optimism and happiness. A brand’s color palette should be carefully selected to align with its brand personality and target audience.
Consistency in color usage across all brand touchpoints is crucial for reinforcing brand recognition and building a cohesive brand experience. Inconsistency can confuse consumers and dilute the brand’s message, weakening its competitive edge.
Typography’s Role in Brand Communication
Typography, the art and technique of arranging type, significantly influences a brand’s visual identity and communication. Font choices convey specific messages about a brand’s personality and target audience. Serif fonts often project a sense of tradition and sophistication, while sans-serif fonts tend to communicate modernity and simplicity. The choice of font size, weight, and spacing also impacts readability and overall aesthetic appeal.
A well-chosen typeface contributes to brand recognition and reinforces the brand’s message, enhancing its competitive standing. Inconsistent or poorly chosen typography can undermine a brand’s credibility and weaken its visual appeal.
Visual Consistency Across Brand Touchpoints
Maintaining visual consistency across all brand touchpoints—from website and social media to packaging and marketing materials—is paramount for building a strong and recognizable brand. This consistency reinforces brand recognition, strengthens brand recall, and cultivates a cohesive brand experience. A consistent visual identity helps consumers quickly identify and connect with the brand, leading to increased brand loyalty and preference.
Inconsistency, on the other hand, can confuse consumers, dilute the brand message, and weaken the brand’s competitive position. Maintaining visual consistency requires meticulous planning and execution across all aspects of the brand’s visual communication.
Successfully harnessing competitive advantage through branding requires a holistic approach, encompassing a clearly defined brand identity, strategic communication, and a deep understanding of the target audience. By consistently delivering a positive customer experience and meticulously tracking key performance indicators, businesses can solidify their market position and achieve sustainable growth. The journey to building a powerful brand is an ongoing process of refinement and adaptation, requiring continuous monitoring and strategic adjustments to navigate the ever-evolving competitive landscape.
Top FAQs
What is the difference between brand awareness and brand equity?
Brand awareness is simply knowing a brand exists. Brand equity encompasses the overall value associated with the brand, including its reputation, customer loyalty, and perceived quality, translating into tangible financial benefits.
How can small businesses compete with larger brands?
Small businesses can leverage niche marketing, focus on building strong customer relationships, and utilize cost-effective digital marketing strategies to build a strong brand presence and compete effectively.
How important is visual consistency in branding?
Visual consistency is crucial. It reinforces brand recognition, builds trust, and creates a cohesive brand experience across all touchpoints, ultimately strengthening brand equity and competitive advantage.
What are some common mistakes businesses make in branding?
Common mistakes include inconsistent messaging, neglecting customer feedback, failing to define a clear target audience, and underestimating the importance of visual identity.