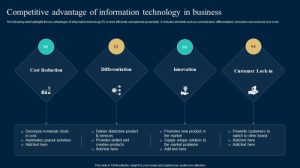
In today’s dynamic marketplace, sustainable growth hinges on a company’s ability to cultivate and maintain a distinct competitive advantage. This requires more than simply offering a good product; it demands a strategic approach to innovation that resonates deeply with customer needs and anticipates future market trends. This exploration delves into the multifaceted strategies involved in building and sustaining such an advantage, examining the role of various innovation types, technological integration, and the importance of a robust organizational culture.
We will analyze established frameworks for competitive advantage, explore real-world examples of companies that have successfully leveraged innovation, and Artikel practical steps for businesses seeking to embed a culture of innovation. The discussion will also address crucial considerations like intellectual property protection, risk assessment, and adapting to market shifts to ensure long-term success.
Defining Competitive Advantage
A competitive advantage represents a firm’s ability to consistently outperform its rivals, creating and capturing greater value for itself. This advantage isn’t simply about being better; it’s about creating a sustainable edge that competitors struggle to replicate or overcome. This sustainability is key, differentiating a fleeting advantage from a truly powerful, long-term benefit.A sustainable competitive advantage rests on several core components.
Firstly, it requires valuable resources and capabilities that are rare, inimitable, and non-substitutable – a framework often referred to as the VRIN framework. Secondly, it demands a strong strategic positioning within the market, leveraging these resources effectively to meet customer needs better than the competition. Finally, it necessitates organizational effectiveness in implementing and adapting strategies to maintain this edge over time.
Adaptability is crucial, as market dynamics constantly shift.
Examples of Companies with Strong Competitive Advantages
Apple’s strong competitive advantage in the smartphone market stems from its combination of brand loyalty, a seamless ecosystem of products and services (iPhones, Macs, iPads, Apple Watch, and related software), and a highly effective marketing strategy. This creates a powerful network effect, making switching costs high for consumers. Similarly, Amazon dominates online retail through its vast selection, efficient logistics network, and customer-centric approach, fostered by its robust data analytics and personalized recommendations.
These companies have built their advantages through continuous innovation and strategic investments, creating barriers to entry for competitors.
Comparison of Frameworks for Analyzing Competitive Advantage
Porter’s Five Forces model focuses on analyzing the competitive intensity of an industry by examining factors like the threat of new entrants, bargaining power of suppliers and buyers, threat of substitutes, and rivalry among existing competitors. This framework helps identify the overall attractiveness of an industry and potential sources of competitive advantage within it. In contrast, the Resource-Based View (RBV) focuses on a firm’s internal resources and capabilities as the primary source of competitive advantage.
RBV emphasizes the importance of unique, valuable, and hard-to-imitate resources in achieving sustained competitive performance. While Porter’s model looks at the external environment, RBV delves into the internal capabilities of the firm. Both frameworks offer valuable insights, and a comprehensive analysis often involves integrating both perspectives.
Hypothetical Business Model: A Sustainable Competitive Advantage Based on Innovation
Imagine a company, “GreenTech Solutions,” developing and marketing sustainable, AI-powered agricultural solutions for small-scale farmers. Their competitive advantage lies in their proprietary AI algorithms that optimize crop yields using minimal water and fertilizer, reducing environmental impact significantly. This innovative technology is protected by patents, making it difficult for competitors to replicate. Furthermore, GreenTech Solutions builds a strong network effect by creating a community platform for farmers to share data and best practices, fostering loyalty and increasing the value of their service.
This business model combines technological innovation with a strong community-building strategy, creating a sustainable competitive advantage in a growing market focused on sustainability and precision agriculture. The company’s value proposition centers around increased crop yields, reduced environmental impact, and a supportive community, making it highly attractive to environmentally conscious farmers.
Innovation as a Driver of Competitive Advantage
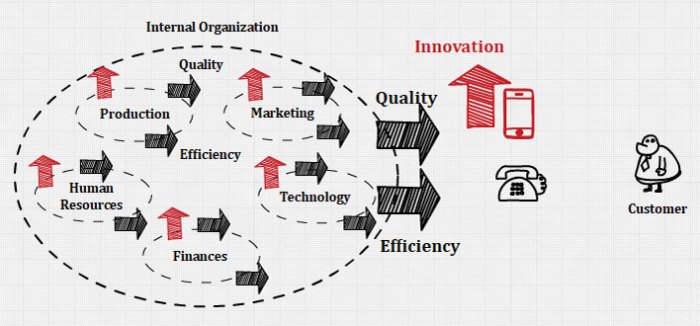
Innovation is no longer a mere advantage; it’s a necessity for survival in today’s dynamic business landscape. Companies that consistently innovate, adapting and evolving to meet changing customer needs and market demands, are far more likely to establish and maintain a powerful competitive advantage. This stems from the ability to create unique value propositions that resonate with customers and distinguish a company from its rivals.
The types of innovation employed, however, significantly impact the nature and sustainability of that advantage.Innovation, in its various forms, fuels competitive advantage by creating new markets, improving existing products and services, and enhancing operational efficiency. This allows businesses to command premium prices, increase market share, and achieve higher profitability, ultimately leading to sustained growth and a strong competitive position.
Understanding the different types of innovation and their respective impacts is crucial for strategizing effective competitive advantage.
Types of Innovation and Their Impact on Competitive Advantage
Different types of innovation offer distinct paths to competitive advantage. Incremental innovation focuses on making small, iterative improvements to existing products or processes. This approach is valuable for enhancing efficiency, reducing costs, and improving customer satisfaction gradually. Radical innovation, on the other hand, involves creating entirely new products, services, or business models that disrupt existing markets. This type of innovation can lead to significant competitive leaps, often creating entirely new market segments.
Disruptive innovation, a subset of radical innovation, focuses on initially targeting underserved or neglected market segments with simpler, more affordable offerings before eventually displacing established players.For example, Apple’s continuous improvement of its iPhone through incremental innovation (better cameras, faster processors, improved software) maintains its competitive edge within the smartphone market. Meanwhile, the introduction of the iPhone itself was a radical innovation that significantly disrupted the existing mobile phone industry.
Similarly, Netflix’s shift from DVD rentals to on-demand streaming was a disruptive innovation that redefined the entertainment industry. This showcases the diverse approaches to innovation and their varied contributions to competitive advantage.
Innovation and Value Creation for Customers
The core of any successful innovation strategy lies in its ability to create value for the customer. This value isn’t solely defined by price; it encompasses the entire customer experience, including product functionality, usability, reliability, and overall satisfaction. Innovative solutions address unmet needs, solve existing problems more effectively, or create entirely new possibilities for customers. This leads to increased customer loyalty, positive word-of-mouth referrals, and a stronger brand reputation – all key components of a robust competitive advantage.For instance, consider the impact of Tesla’s electric vehicles.
They not only offer a cleaner alternative to traditional gasoline-powered cars but also provide a superior driving experience with advanced technology and features. This combination of environmental responsibility and enhanced functionality creates significant value for customers, setting Tesla apart from its competitors.
Identifying Unmet Customer Needs and Translating Them into Innovative Solutions
The process of translating unmet customer needs into innovative solutions requires a deep understanding of customer behavior, market trends, and technological advancements. This often involves a combination of market research, customer feedback analysis, and brainstorming sessions. Identifying these needs might involve techniques like surveys, focus groups, ethnographic studies, and analyzing customer reviews and social media sentiment. Once these needs are identified, the next step involves developing creative solutions that address them effectively.
This often requires a multidisciplinary approach, combining expertise from various fields like engineering, design, and marketing.For example, consider the development of the Nintendo Wii. Nintendo identified a market need for a gaming console that was accessible to a broader audience, including those who were not hardcore gamers. This led to the development of motion-controlled gaming, a novel approach that catered to a wider range of players and helped establish the Wii as a highly successful product.
This illustrates how understanding and addressing unmet customer needs is a critical component of creating a successful and impactful innovation.
Strategies for Building a Competitive Advantage Through Innovation
Building a sustainable competitive advantage requires a proactive and strategic approach to innovation. It’s not enough to simply be innovative; the innovation must be aligned with business goals and effectively implemented to deliver tangible results. This involves a structured process, careful risk assessment, and robust measurement to track progress and demonstrate return on investment.
Developing an Innovation Strategy Aligned with Business Goals
A successful innovation strategy begins with a clear understanding of the organization’s overall business objectives. This involves identifying market opportunities, analyzing competitive landscapes, and defining specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals for innovation initiatives. The strategy should then Artikel the resources, processes, and metrics necessary to achieve these goals. This ensures that innovation efforts are focused and contribute directly to the company’s bottom line.
For example, a company aiming for market leadership might prioritize disruptive innovations, while a company focused on cost reduction might focus on process improvements and efficiency gains.
Implementing an Innovation Process Within an Organization
Implementing an innovation process requires a systematic approach. This involves establishing a dedicated innovation team or department, defining clear roles and responsibilities, and creating a culture that encourages experimentation and risk-taking. A phased approach, from idea generation to market launch, is crucial. This might involve brainstorming sessions, prototyping, pilot testing, and iterative refinement based on customer feedback.
Establishing a robust project management system is also vital to track progress, manage resources, and ensure timely execution. Regular communication and feedback loops are key to maintaining momentum and addressing challenges proactively.
Assessing the Potential Risks and Rewards of Innovation Initiatives
Every innovation initiative carries inherent risks and potential rewards. A comprehensive framework for assessing these is essential. This framework should consider factors such as market demand, technological feasibility, competitive landscape, financial investment required, and potential return on investment (ROI). Techniques like SWOT analysis, scenario planning, and risk registers can help identify potential challenges and opportunities. For example, a new product launch might involve risks related to manufacturing delays, negative customer reviews, or intense competition.
However, the potential rewards could include increased market share, enhanced brand reputation, and significant revenue growth. A thorough risk assessment allows for proactive mitigation strategies and informed decision-making.
Measuring the Success of Innovation Efforts
Measuring the success of innovation initiatives requires a clear set of metrics aligned with the overall business goals. These metrics should be tracked consistently to monitor progress and demonstrate the impact of innovation efforts on competitive advantage. The following table illustrates key metrics, targets, measurement methods, and potential results:
| Metric | Target | Measurement Method | Results |
|---|---|---|---|
| Market Share | Increase by 10% within 2 years | Sales data, market research reports | Actual increase in market share (e.g., 8%, 12%) |
| Customer Satisfaction | Improve Net Promoter Score (NPS) by 15 points | Customer surveys, feedback analysis | Change in NPS score (e.g., +12 points, +18 points) |
| Return on Investment (ROI) | Achieve a 20% ROI within 3 years | Financial modeling, cost-benefit analysis | Actual ROI achieved (e.g., 18%, 25%) |
| Time to Market | Reduce time to market by 25% | Project timelines, launch dates | Actual reduction in time to market (e.g., 20%, 30%) |
The Role of Technology in Building Competitive Advantage
Technology’s impact on business is undeniable, profoundly shaping competitive landscapes. The strategic adoption of emerging technologies isn’t just about keeping up; it’s about forging a decisive advantage, driving innovation, and ultimately, achieving sustainable growth. This section explores how leveraging technology translates into a powerful competitive edge.
Emerging technologies, such as Artificial Intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT), and advanced data analytics, are reshaping industries at an unprecedented pace. These tools offer businesses the potential to optimize operations, personalize customer experiences, and create entirely new products and services. The companies that successfully integrate these technologies into their strategies are often those that experience the most significant gains in market share and profitability.
Impact of Emerging Technologies on Competitive Advantage
The integration of AI, IoT, and advanced analytics provides numerous avenues for competitive differentiation. AI-powered automation can streamline processes, reducing costs and improving efficiency. IoT devices provide valuable real-time data, enabling businesses to make data-driven decisions and personalize offerings. Advanced analytics allow for predictive modeling, facilitating proactive responses to market trends and customer needs. For example, a manufacturing company using AI-powered predictive maintenance can minimize downtime and optimize production schedules, resulting in significant cost savings and improved output.
A retailer using IoT sensors to track inventory levels in real-time can avoid stockouts and optimize supply chain management.
Examples of Companies Successfully Leveraging Technology
Netflix’s use of sophisticated recommendation algorithms, powered by AI, has revolutionized the entertainment industry. By personalizing content suggestions, they have cultivated unparalleled user engagement and loyalty, setting a new standard for personalized user experiences. Tesla’s integration of advanced technology, including AI-driven autonomous driving features and over-the-air software updates, has disrupted the automotive industry, pushing the boundaries of innovation and creating a highly desirable brand.
Amazon’s utilization of AI-powered logistics and predictive analytics has significantly optimized its supply chain, leading to faster delivery times and reduced costs.
Best Practices for Integrating New Technologies
Successful technology integration requires a strategic and phased approach. It begins with a clear understanding of business needs and objectives. Companies should prioritize technologies that directly address critical pain points and align with overall business goals. A pilot program approach, starting with a small-scale implementation before wider deployment, allows for testing, refinement, and risk mitigation. Investing in employee training and development is crucial to ensure effective adoption and utilization of new technologies.
Collaboration between IT departments and business units is essential to ensure seamless integration and avoid silos. Finally, continuous monitoring and evaluation are necessary to track progress, identify areas for improvement, and adapt to changing technological landscapes.
Challenges Associated with Technology Adoption and Strategies for Overcoming Them
The adoption of new technologies presents several challenges. High initial investment costs can be a significant barrier, requiring careful financial planning and potentially seeking external funding. Data security and privacy concerns are paramount, necessitating robust security measures and compliance with relevant regulations. Resistance to change within an organization can hinder adoption, necessitating effective change management strategies, including clear communication, employee training, and addressing concerns proactively.
Integration complexities can arise when merging new technologies with existing systems, requiring careful planning and potentially custom software development. Overcoming these challenges requires a well-defined strategy, strong leadership, and a commitment to continuous learning and adaptation.
Protecting and Sustaining Competitive Advantage

Building a competitive advantage through innovation is only half the battle; sustaining that advantage requires a proactive and multifaceted approach. Protecting intellectual property, cultivating strong organizational capabilities, fostering a culture of innovation, and adapting to market shifts are all critical components of long-term success. Without these elements, even the most groundbreaking innovations can be quickly overtaken by competitors.Protecting intellectual property is paramount to maintaining a competitive edge.
It ensures that the fruits of innovation remain exclusive, preventing competitors from easily replicating successful products or processes. This protection can take many forms, including patents, trademarks, copyrights, and trade secrets. Each offers a unique level of protection, tailored to different types of intellectual property. For example, a pharmaceutical company might rely heavily on patents to protect its novel drug formulations, while a software company might use copyrights to safeguard its source code.
A robust intellectual property strategy requires careful consideration of the specific type of intellectual property, the geographic scope of protection, and the enforcement mechanisms available. Failure to adequately protect intellectual property can lead to significant losses, both financially and strategically.
Intellectual Property Protection Strategies
A comprehensive intellectual property strategy involves more than simply filing patents. It requires a proactive approach to identifying, protecting, and enforcing intellectual property rights throughout the entire innovation lifecycle. This includes regular assessments of the intellectual property portfolio, identifying potential infringement, and developing effective strategies for responding to infringement claims. Furthermore, a clear understanding of the legal landscape surrounding intellectual property is crucial, ensuring compliance with relevant laws and regulations.
This may involve collaborating with intellectual property lawyers and regularly reviewing the company’s intellectual property policies. Strong documentation practices, meticulous record-keeping of inventions and innovations, and proactive engagement with relevant legal and regulatory bodies are also critical aspects of an effective strategy.
Building Organizational Capabilities for Continuous Innovation
Sustaining a competitive advantage necessitates a continuous cycle of innovation. This requires building strong organizational capabilities that support the entire innovation process, from idea generation to market launch and beyond. This includes investing in research and development, fostering collaboration between different departments, and establishing clear processes for evaluating and implementing new ideas. Crucially, it also involves creating an environment where experimentation and risk-taking are encouraged, even if some initiatives fail.
Learning from both successes and failures is vital for continuous improvement. For example, a company might establish dedicated innovation teams, provide employees with training in design thinking and other innovation methodologies, and create a system for tracking and measuring the impact of innovation initiatives.
Fostering a Culture of Innovation
Organizational culture plays a significant role in driving innovation. A culture that values creativity, collaboration, and risk-taking is essential for generating and implementing new ideas. This requires strong leadership that champions innovation, empowers employees to take ownership of projects, and rewards both successes and learning from failures. Open communication, feedback mechanisms, and a willingness to embrace change are all crucial elements of an innovative culture.
Companies can actively foster this culture through various initiatives, such as employee suggestion programs, hackathons, cross-functional teams, and leadership training programs focused on innovation management. Furthermore, celebrating successes and learning from failures publicly reinforces the importance of innovation within the organization.
Adapting to Market Changes and Maintaining Long-Term Competitive Advantage
Markets are dynamic and constantly evolving. Maintaining a long-term competitive advantage requires a proactive approach to monitoring market trends, anticipating future changes, and adapting strategies accordingly. This involves regularly conducting market research, analyzing competitor activities, and tracking technological advancements. A flexible organizational structure and agile processes are essential for responding quickly to market changes. Companies might use scenario planning to anticipate potential future scenarios and develop contingency plans.
They might also invest in technologies that enhance their agility and adaptability, such as data analytics tools that provide real-time insights into market trends. For example, a company facing increased competition from a new technology might choose to invest in research and development to develop its own competing technology or pivot its business model to focus on a different market segment.
Continuous monitoring of the competitive landscape and adapting to market dynamics is crucial for long-term success.
Case Studies
This section examines three companies—Apple, Tesla, and Netflix—that have successfully leveraged innovation to build and maintain a significant competitive advantage. Each case study details their innovative strategies, the resulting impact on their market position, and the challenges they encountered along the way. Analyzing these diverse examples reveals valuable insights into effective innovation management and the factors contributing to long-term success.
Apple: Innovation Through Ecosystem Integration
Apple’s competitive advantage stems from its tightly integrated ecosystem of hardware, software, and services. This strategy, built on consistent innovation across these areas, creates a powerful network effect, locking in customers and making switching costs high.
- Innovation Strategy: Focus on user experience, seamless integration between devices (iPhone, iPad, Mac), and a curated app store. Continuous improvement in hardware design and performance, coupled with regular software updates, maintains a premium brand image.
- Impact: Dominance in the smartphone and tablet markets, a highly profitable services business, and a fiercely loyal customer base. Apple consistently commands premium pricing, reflecting the perceived value of its ecosystem.
- Challenges Faced: Maintaining innovation momentum in mature markets, competition from Android devices offering similar features at lower prices, and balancing user privacy concerns with data collection for service improvement.
Tesla: Disruptive Innovation in the Automotive Industry
Tesla’s success is a testament to disruptive innovation. By focusing on electric vehicles (EVs) and integrating advanced technologies, Tesla challenged established automakers and redefined the automotive landscape.
- Innovation Strategy: Pioneering battery technology, autonomous driving capabilities, and a direct-to-consumer sales model, bypassing traditional dealerships. Emphasis on sustainability and a forward-thinking brand image.
- Impact: Significant growth in the EV market, a shift in consumer perception of electric vehicles, and the establishment of Tesla as a leading technology company. The company has significantly impacted the broader automotive industry, forcing traditional manufacturers to accelerate their EV development.
- Challenges Faced: Production bottlenecks, maintaining consistent quality control, managing supply chain complexities, and navigating regulatory hurdles in different markets. Competition from established automakers entering the EV market is also intensifying.
Netflix: Transforming the Entertainment Industry Through Streaming
Netflix’s innovation lies in its pioneering role in streaming video on demand (SVOD). By disrupting traditional television and movie rental models, Netflix created a new entertainment paradigm.
- Innovation Strategy: Early adoption of streaming technology, development of original content, personalized recommendations, and a user-friendly interface. Continuous investment in technology and content creation to maintain a competitive edge.
- Impact: Transformation of the television and film industry, global reach with a massive subscriber base, and a significant impact on how people consume entertainment. The company has significantly altered the landscape of content creation and distribution.
- Challenges Faced: Competition from other streaming services, managing content costs, balancing subscriber growth with profitability, and adapting to evolving consumer preferences and technological advancements. Maintaining the quality of original content and addressing concerns about content diversity are also ongoing challenges.
Ultimately, building a competitive advantage through innovation is a continuous journey, not a destination. It demands a commitment to understanding customer needs, embracing new technologies, fostering a culture of experimentation, and adapting to the ever-evolving market landscape. By strategically implementing the principles discussed, businesses can not only survive but thrive, establishing a sustainable competitive edge that ensures long-term success and growth.
FAQ Section
What is the difference between incremental and radical innovation?
Incremental innovation involves making small, iterative improvements to existing products or services, while radical innovation involves creating entirely new products or services that disrupt the market.
How can I measure the ROI of innovation initiatives?
Measuring ROI requires defining clear metrics tied to business goals (e.g., increased market share, improved customer satisfaction, reduced costs). Track these metrics before, during, and after implementing innovation initiatives to assess their impact.
How do I foster a culture of innovation within my organization?
Encourage experimentation, provide resources for innovation projects, reward risk-taking, and create an environment where employees feel comfortable sharing ideas and challenging the status quo. Leadership buy-in is crucial.
What are some common pitfalls to avoid when pursuing innovation?
Common pitfalls include neglecting market research, underestimating the resources needed, failing to protect intellectual property, and a lack of clear metrics for measuring success. Ignoring employee input is also detrimental.