Maintaining a competitive edge in today’s rapidly evolving business landscape is a constant challenge. Success hinges not merely on initial market entry but on the ability to adapt, innovate, and consistently outperform competitors over the long term. This exploration delves into the multifaceted strategies required to build and sustain a truly enduring competitive advantage, examining key factors from operational excellence to strategic foresight.
We will explore proven frameworks for analyzing competitive landscapes, the critical role of innovation and technology, and the importance of cultivating strong customer relationships and a highly skilled workforce. Understanding how to effectively manage resources, anticipate market shifts, and leverage competitive intelligence will be crucial in our journey towards long-term success. This guide aims to equip you with the knowledge and strategic tools necessary to navigate the complexities of maintaining a competitive advantage, transforming challenges into opportunities for sustained growth and profitability.
Defining Competitive Advantage
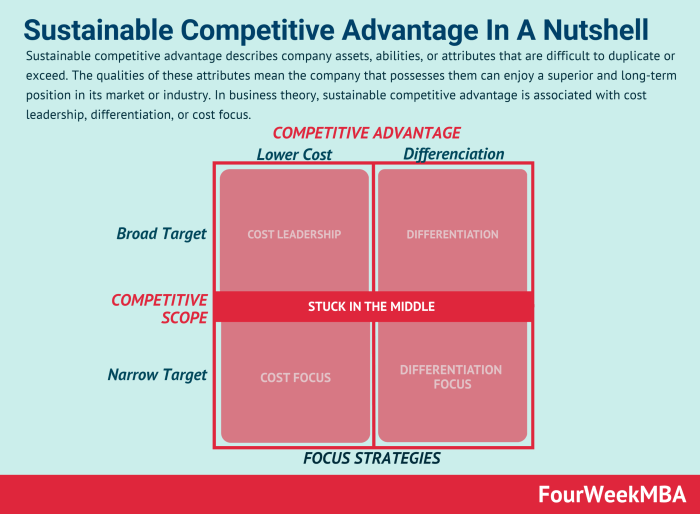
A sustainable competitive advantage allows a firm to outperform its rivals over a prolonged period. It’s not merely about being better today; it’s about building a position that’s difficult for competitors to replicate or overcome. This requires a deep understanding of the market, the firm’s unique capabilities, and the dynamics of competition.A sustainable competitive advantage hinges on several core components.
First, it requires a valuable offering – a product or service that customers desire and are willing to pay for. Second, it needs to be rare; not readily available to competitors. Third, it must be inimitable, meaning difficult or costly for others to copy. Finally, it needs to be non-substitutable, meaning there aren’t readily available alternatives that provide similar value to customers.
These four components—value, rarity, inimitability, and non-substitutability—form the basis of a robust and enduring competitive advantage.
Examples of Companies with Historically Strong Competitive Advantages
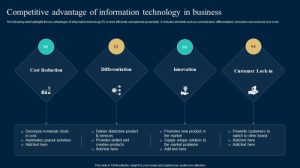
Several companies have demonstrated historically strong competitive advantages. Consider Coca-Cola, whose brand recognition and global distribution network are incredibly difficult to replicate. Their success stems from decades of effective marketing, building an iconic brand that resonates deeply with consumers worldwide. Similarly, Apple has cultivated a strong competitive advantage through its design-centric approach, seamless ecosystem, and loyal customer base.
Their focus on user experience and brand loyalty creates a powerful barrier to entry for competitors. Finally, Walmart’s efficient supply chain and logistical network, coupled with its vast scale, provide a significant cost advantage that is difficult to match. These examples highlight the importance of building a strong brand, fostering customer loyalty, and achieving operational excellence.
Comparison of Frameworks for Analyzing Competitive Advantage
Porter’s Five Forces and the Resource-Based View (RBV) offer distinct but complementary frameworks for analyzing competitive advantage. Porter’s Five Forces focuses on the external environment, examining the competitive intensity of an industry by considering the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of suppliers and buyers, the threat of substitutes, and the rivalry among existing competitors. The RBV, on the other hand, emphasizes the internal capabilities of a firm, arguing that sustainable competitive advantage stems from possessing valuable, rare, inimitable, and non-substitutable resources and capabilities (VRIN).
While Porter’s model helps assess the attractiveness of an industry, the RBV focuses on identifying the unique strengths within a firm that can lead to sustained success. A comprehensive analysis ideally integrates both perspectives, considering both external industry dynamics and internal organizational capabilities.
Hypothetical Business Model with Robust Competitive Advantage
Imagine a company specializing in personalized, AI-powered educational software for K-12 students. This software adapts to individual learning styles, providing customized lesson plans and real-time feedback. The competitive advantage stems from a combination of factors: a proprietary AI algorithm for personalized learning (rare and inimitable), a large database of curated educational content (valuable and rare), strong partnerships with schools and educators (creating distribution channels difficult to replicate), and a focus on continuous improvement and data-driven refinement of the algorithm (non-substitutable due to constant innovation).
This combination of technological sophistication, educational expertise, and strategic partnerships creates a robust and potentially sustainable competitive advantage in a rapidly evolving educational technology landscape. The company’s value proposition is centered on improved student outcomes and increased efficiency for educators, making it attractive to both students and schools.
Innovation and Technological Advancement
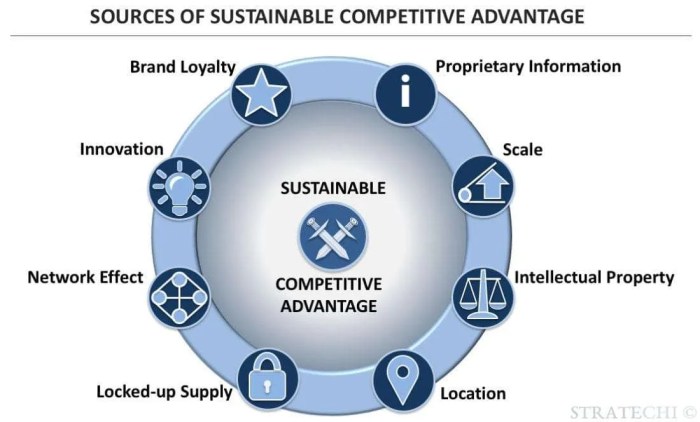
Sustaining a competitive advantage in today’s rapidly evolving marketplace necessitates a commitment to continuous innovation and technological advancement. Companies must not only adapt to new technologies but also proactively leverage them to create new products, services, and business models that outperform the competition. Failure to do so often results in obsolescence and market irrelevance.Continuous innovation acts as a powerful engine for maintaining a competitive edge.
By consistently developing new and improved products, services, and processes, businesses can differentiate themselves from competitors, attract and retain customers, and increase profitability. This process involves not only incremental improvements but also disruptive innovations that fundamentally reshape the industry landscape.
Examples of Companies Leveraging Technology
Several companies have demonstrated the power of technological innovation to sustain their competitive advantage. Amazon, for example, has continuously invested in its e-commerce platform, logistics network, and cloud computing services (Amazon Web Services), creating a powerful ecosystem that is difficult for competitors to replicate. Apple’s success is similarly rooted in its relentless pursuit of technological excellence, evident in its innovative product designs and user-friendly interfaces.
These companies have not only adapted to technological change but have actively shaped it, setting the pace for industry innovation.
Challenges of Managing Technological Disruption
Managing technological disruption and adapting to changing market dynamics presents significant challenges. Companies must be agile and responsive, capable of quickly identifying and responding to emerging technologies and shifts in customer preferences. This requires a culture of innovation, investment in research and development, and a willingness to embrace change. Furthermore, companies must anticipate potential disruptions and develop strategies to mitigate their impact.
A failure to adapt can lead to significant market share loss and even business failure. For example, the rise of smartphones significantly disrupted the market for traditional feature phones, leaving many manufacturers struggling to adapt.
Technological Roadmap for Sustaining Competitive Position
A well-defined technological roadmap is crucial for sustaining a company’s competitive position. This roadmap should Artikel the company’s technological vision, identify key milestones, define timelines, allocate resources, and address potential risks. The roadmap should be dynamic, adapting to changes in the technological landscape and market conditions.
| Milestone | Timeline | Resources | Risk Mitigation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Develop prototype of next-generation product | 12 months | $500,000, Engineering team of 5 | Regular testing and feedback loops; contingency planning for technical setbacks |
| Secure key patents | 18 months | $100,000, Legal team, IP specialists | Thorough patent search; proactive legal action against infringement |
| Launch beta version of product | 24 months | $200,000, Marketing team, Beta testing program | Comprehensive user feedback analysis; iterative improvements based on feedback |
| Full product launch and market entry | 36 months | $1,000,000, Sales team, Marketing campaign | Market research and competitive analysis; flexible pricing and distribution strategies |
Operational Excellence and Efficiency
Sustained competitive advantage hinges not only on innovative products and services but also on the ability to deliver them efficiently and effectively. Operational excellence, encompassing streamlined processes and optimized resource allocation, plays a crucial role in achieving this long-term success. A company’s operational prowess directly impacts its profitability, customer satisfaction, and overall market standing.Operational excellence is built upon a foundation of strategic operational choices and a commitment to continuous improvement.
These strategies, when effectively implemented, create a significant barrier to entry for competitors and solidify a company’s position in the market.
Key Operational Strategies for Sustained Competitive Advantage
Effective operational strategies are multifaceted and interconnected. They require a holistic approach that considers all aspects of the business, from production and logistics to customer service and human resources. The following points highlight key elements of such strategies.
- Process Optimization: This involves streamlining workflows, eliminating bottlenecks, and automating repetitive tasks to improve efficiency and reduce costs. Continuous monitoring and analysis of processes are essential to identify areas for improvement.
- Supply Chain Management: A robust and resilient supply chain ensures the timely and cost-effective delivery of materials and components. This involves close collaboration with suppliers, efficient inventory management, and effective logistics. Strong supply chain management can also lead to enhanced product quality and reduced lead times.
- Technology Integration: Leveraging technology, such as automation, data analytics, and artificial intelligence, can significantly enhance operational efficiency. This can range from automating manufacturing processes to using data analytics to optimize inventory levels and predict demand.
- Talent Development and Employee Engagement: A highly skilled and motivated workforce is critical for operational excellence. Companies need to invest in training and development programs to enhance employee skills and foster a culture of continuous improvement and collaboration.
- Quality Control and Management: Implementing rigorous quality control measures throughout the production process ensures that products and services meet the highest standards. This reduces waste, improves customer satisfaction, and enhances brand reputation.
The Importance of Process Optimization and Supply Chain Management
Process optimization and supply chain management are intrinsically linked and crucial for sustained competitive advantage. Process optimization focuses on internal efficiency, while supply chain management optimizes the flow of goods and services across the entire value chain. Together, they contribute to lower costs, improved quality, and faster delivery times – all key factors in maintaining a competitive edge.For example, a company that optimizes its manufacturing processes to reduce waste and improve efficiency can lower its production costs, allowing it to offer more competitive pricing.
Simultaneously, a well-managed supply chain ensures that the company has the necessary materials and components available when needed, preventing production delays and ensuring timely delivery to customers.
Operational Models and Their Impact on Competitiveness
Various operational models offer different approaches to achieving excellence. The choice of model depends on the industry, company size, and strategic goals.
- Lean Manufacturing: This model focuses on eliminating waste in all aspects of production, from materials and time to effort and space. It emphasizes continuous improvement and involves the active participation of all employees. Lean manufacturing leads to increased efficiency, reduced costs, and improved quality.
- Six Sigma: This data-driven approach aims to reduce defects and variability in processes. It uses statistical methods to identify and eliminate sources of variation, leading to improved quality, reduced costs, and increased customer satisfaction. Six Sigma methodologies are often used in conjunction with lean manufacturing principles.
Case Study: Toyota’s Operational Excellence
Toyota’s sustained success is largely attributed to its commitment to operational excellence. Its lean manufacturing system, known as the Toyota Production System (TPS), has become a benchmark for many industries.
- Just-in-Time (JIT) Inventory Management: Minimizes inventory holding costs and reduces waste by receiving materials only when needed.
- Kaizen (Continuous Improvement): Fosters a culture of continuous improvement through small, incremental changes suggested by employees at all levels.
- Jidoka (Automation with a Human Touch): Combines automation with human oversight to ensure quality and prevent defects.
- Andon System: Allows workers to immediately stop the production line if a problem is detected, preventing the production of defective products.
- Respect for People: Values employee contributions and fosters a culture of teamwork and collaboration.
Financial Strength and Resource Management
A company’s financial health is intrinsically linked to its ability to sustain a competitive advantage. Strong financial management provides the resources necessary for innovation, operational efficiency, and strategic investments, ultimately bolstering a company’s long-term competitiveness in the marketplace. Without a solid financial foundation, even the most brilliant strategies can falter.Effective financial management ensures a company can weather economic downturns, invest in growth opportunities, and maintain a competitive edge through strategic resource allocation.
This involves careful budgeting, efficient cost management, and prudent financial planning. A strong balance sheet provides the flexibility to seize opportunities and respond to challenges, while consistent profitability provides the fuel for sustained growth and competitive advantage.
Effective Resource Allocation Enhances Competitiveness
Effective resource allocation involves strategically distributing capital, human resources, and technological assets to maximize their impact on the business’s competitive position. This requires a deep understanding of the market, the company’s strengths and weaknesses, and the potential returns on different investment opportunities. For instance, a company might choose to allocate more resources to research and development if it anticipates significant technological breakthroughs in its industry, or it might invest in marketing and sales if it is launching a new product.
Alternatively, streamlining inefficient processes, improving supply chain management, and focusing on high-margin products are all examples of effective resource allocation that contribute to competitiveness. Consider a hypothetical scenario: Company A, focusing on efficiency, invests in automation, reducing production costs by 15% and undercutting competitors’ pricing. Company B, focusing on R&D, allocates funds to develop a groundbreaking new technology that establishes a new market segment, creating significant first-mover advantage.
Both demonstrate effective resource allocation, leading to enhanced competitiveness through different strategies.
Strategic Investments in Research and Development
Investing in research and development (R&D) is crucial for long-term competitive advantage. R&D fuels innovation, allowing companies to develop new products, improve existing ones, and create entirely new markets. This investment leads to patents, proprietary technologies, and a strong intellectual property portfolio, which act as significant barriers to entry for competitors. For example, pharmaceutical companies invest heavily in R&D to discover and develop new drugs, giving them a significant competitive advantage.
Similarly, technology companies invest in R&D to create innovative software and hardware, maintaining their leadership positions. The returns from R&D investments are often long-term and may not be immediately apparent, but they are essential for sustained competitiveness in rapidly evolving industries.
A Financial Model Illustrating Long-Term Impact of Strategic Resource Management
Imagine a simplified model where Company X invests 10% of its annual revenue in R&D for five years. This investment leads to a 2% annual increase in revenue growth beyond the initial investment period (years 6-10). We can illustrate this using a simple table:
| Year | Revenue (Millions) | R&D Investment (Millions) | Revenue Growth (Millions) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1-5 | Assume constant annual revenue, say $100 million | $10 million annually | 0 |
| 6 | $102 million (2% increase) | 0 | $2 million |
| 7 | $104.04 million (2% increase) | 0 | $2.04 million |
| 8 | $106.12 million (2% increase) | 0 | $2.08 million |
| 9 | $108.24 million (2% increase) | 0 | $2.12 million |
| 10 | $110.41 million (2% increase) | 0 | $2.17 million |
This simplified model demonstrates how strategic investment in R&D, even with a short-term cost, can lead to significant long-term revenue growth and a sustained competitive advantage. The actual financial impact will vary depending on several factors, including the industry, the effectiveness of the R&D, and the overall economic climate. However, the model illustrates the principle that strategic resource management, including investments in R&D, can significantly enhance a company’s long-term competitiveness.
Competitive Intelligence and Market Analysis

Sustaining a competitive advantage requires a deep understanding of the competitive landscape and market dynamics. Competitive intelligence and market analysis provide the crucial insights needed to anticipate changes, identify opportunities, and proactively adapt strategies to maintain a leading position. This involves more than simply tracking competitors; it’s about understanding market trends, customer behavior, and emerging technologies to inform strategic decision-making.Competitive intelligence gathering and market analysis are vital for proactive decision-making and sustained competitive advantage.
By systematically collecting and analyzing data, businesses can identify emerging threats and opportunities, develop effective competitive response strategies, and ultimately, improve their chances of long-term success. Ignoring these crucial aspects can lead to missed opportunities and a decline in market share.
Methods for Identifying Emerging Threats and Opportunities
Effective competitive intelligence relies on a multifaceted approach to data gathering and analysis. This includes monitoring competitor activities, analyzing market trends, and assessing technological advancements. For example, a company might use publicly available information like press releases and annual reports to track a competitor’s new product launches and marketing campaigns. They might also conduct customer surveys to understand evolving needs and preferences, revealing potential market opportunities or identifying vulnerabilities in their own offerings.
Furthermore, monitoring industry publications and attending trade shows can provide insights into emerging technologies and shifts in market demand. These insights can then be synthesized to identify potential threats – such as a new competitor entering the market with a disruptive technology – or opportunities – such as an underserved niche segment with high growth potential.
Developing Effective Competitive Response Strategies
Once threats and opportunities have been identified, businesses must develop appropriate response strategies. This involves assessing the severity of threats and the potential of opportunities, and then formulating plans to mitigate risks and capitalize on promising areas. For example, if a competitor launches a significantly improved product, a company might respond by accelerating its own R&D efforts, improving its product features, or focusing on a different market segment.
If a new market opportunity emerges, the company might develop a new product line or expand into that segment. Effective response strategies often involve a combination of offensive and defensive tactics, carefully tailored to the specific competitive context. A SWOT analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats) can be a useful tool in this process, helping to align strategic responses with the company’s internal capabilities and external environment.
Designing a Competitive Intelligence System
A robust competitive intelligence system is crucial for sustained competitive advantage. This system should incorporate several key components. First, it needs a clear definition of the scope and objectives of intelligence gathering. What information is most critical for the business? What specific competitors and market segments need to be monitored?
Second, the system should establish reliable data sources and collection methods. This could include online databases, industry reports, market research firms, customer feedback mechanisms, and even dedicated competitive intelligence professionals. Third, the system must incorporate effective data analysis techniques. This might involve statistical analysis, trend forecasting, and scenario planning. Finally, the system should have a mechanism for disseminating actionable insights to relevant decision-makers within the organization, ensuring the information is used to inform strategic decisions and improve business performance.
A well-designed system allows for proactive responses to market changes, preventing reactive and potentially costly adjustments. Consider a pharmaceutical company constantly monitoring clinical trials of competitors’ drugs. This allows them to adjust their own R&D pipeline, potentially speeding up development or shifting focus based on emerging competitor data.
Sustaining a competitive advantage is not a destination, but a continuous journey requiring vigilance, adaptability, and a commitment to excellence. By integrating the strategies discussed—from operational efficiency and strategic innovation to robust customer relationships and effective talent management—businesses can build a resilient foundation for long-term success. Continuous monitoring of the competitive landscape, proactive adaptation to market shifts, and a relentless pursuit of improvement are key to navigating the dynamic forces shaping the modern business world and securing a lasting competitive edge.
Popular Questions
What is the most important factor in sustaining a competitive advantage?
There’s no single “most important” factor; it’s a combination. However, adaptability and a commitment to continuous improvement are consistently crucial. The specific mix depends heavily on the industry and competitive landscape.
How can small businesses compete with larger corporations?
Small businesses can leverage agility, niche specialization, superior customer service, and innovative approaches to compete effectively. Focusing on a specific target market and building strong brand loyalty can be particularly advantageous.
What role does luck play in maintaining a competitive advantage?
While some elements of success involve fortunate timing or circumstances, sustained competitive advantage relies primarily on strategic planning, execution, and adaptability. Luck may provide initial opportunities, but consistent performance is key to long-term success.