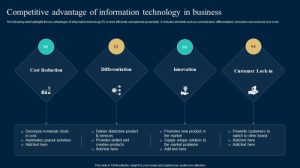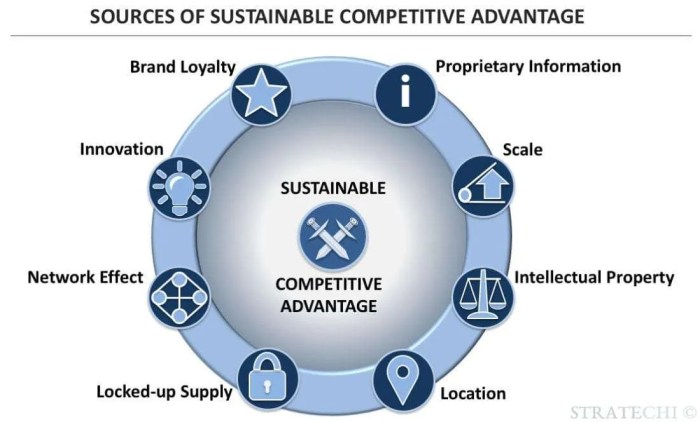
Securing a sustainable competitive advantage is the holy grail for businesses striving for long-term success. This pursuit involves a deep understanding of market dynamics, resource allocation, and strategic maneuvering. It’s not merely about outperforming competitors today; it’s about building a resilient foundation that withstands the test of time and evolving market landscapes. This exploration delves into the core principles, strategic frameworks, and practical applications of building and sustaining a competitive edge.
We’ll examine various approaches, from cost leadership and differentiation to niche market focus, analyzing real-world examples of companies that have successfully implemented these strategies. Furthermore, we will explore the critical role of resources, capabilities, and innovation in achieving and maintaining a lasting competitive advantage in an increasingly dynamic business environment. The discussion will also address the challenges involved in sustaining this advantage in the face of evolving market conditions and technological advancements.
Analyzing the Competitive Landscape
Understanding the competitive landscape is crucial for developing a sustainable competitive advantage. A thorough analysis allows businesses to identify opportunities, threats, and the relative strengths and weaknesses of their competitors, ultimately informing strategic decision-making. This analysis should be dynamic, regularly reviewed and updated to reflect changes in the market.
The Competitive Landscape of the Electric Vehicle (EV) Industry
The electric vehicle (EV) industry is experiencing rapid growth and significant shifts in its competitive landscape. Several key factors shape this dynamic environment. These include technological advancements (battery technology, charging infrastructure), government regulations (emission standards, subsidies), consumer preferences (environmental concerns, cost considerations), and the established presence of legacy automotive manufacturers alongside emerging EV-focused companies. The interplay of these factors creates a complex and ever-evolving competitive arena.
Porter’s Five Forces and Sustainable Advantage in the EV Industry
Porter’s Five Forces framework provides a valuable lens for understanding the competitive dynamics within the EV industry. By analyzing the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of suppliers and buyers, the threat of substitute products, and the intensity of rivalry among existing competitors, companies can gain insights into the overall attractiveness and profitability of the industry.The threat of new entrants is relatively high due to the lower barriers to entry compared to traditional automotive manufacturing (e.g., less reliance on extensive physical infrastructure).
The bargaining power of suppliers (battery manufacturers, raw material providers) is significant, particularly given the strategic importance of battery technology. Buyer power is also considerable, with consumers increasingly price-sensitive and discerning about vehicle features and performance. The threat of substitutes is present from continued improvements in internal combustion engine technology and alternative transportation options (public transit, cycling). Finally, rivalry among existing competitors is intense, with established automakers and new EV startups vying for market share.
Understanding these forces allows companies to develop strategies that mitigate threats and leverage opportunities to achieve sustainable competitive advantage. For instance, a company might focus on vertical integration to reduce supplier dependence or invest heavily in R&D to differentiate its products and reduce the threat of substitutes.
Examples of Companies Adapting to Changing Competitive Landscapes
Tesla, an early entrant in the EV market, successfully adapted its strategy by focusing on technological innovation, creating a strong brand identity, and developing a direct-to-consumer sales model, bypassing traditional dealerships. This allowed them to build a significant first-mover advantage. Conversely, established automakers like Volkswagen and General Motors have responded to the growing popularity of EVs by investing heavily in electric vehicle development and production, leveraging their existing manufacturing capabilities and distribution networks.
These companies are adapting to the changing competitive landscape by strategically incorporating electric vehicles into their broader portfolios.
Analysis of the EV Industry Competitive Landscape
| Factor | Impact on Competition | Examples | Mitigation Strategies |
|---|---|---|---|
| Technological Advancements (Battery Technology) | Creates significant competitive advantage for companies with superior battery technology. Drives innovation and cost reduction. | Tesla’s battery technology, CATL’s battery production capacity | Invest heavily in R&D, strategic partnerships with battery technology providers, vertical integration |
| Government Regulations (Emission Standards) | Shapes demand and influences the viability of different vehicle types. Creates opportunities for companies that meet stricter standards. | EU emission regulations, US clean vehicle standards | Compliance with regulations, lobbying for favorable policies, developing vehicles that exceed regulatory requirements |
| Consumer Preferences (Environmental Concerns) | Drives demand for EVs, but also creates pressure for competitive pricing and performance. | Growing consumer demand for sustainable transportation, increasing awareness of climate change | Focus on sustainability messaging, offer competitive pricing and performance, emphasize vehicle features aligned with consumer preferences |
| Intensity of Rivalry | High due to the presence of both established automakers and new entrants. Leads to price competition and innovation. | Competition between Tesla, Volkswagen, and other EV manufacturers | Differentiation through technology, brand building, unique customer experiences, strategic alliances |
Competitive Advantage
A competitive advantage is what sets a business apart from its rivals, allowing it to achieve higher profitability and greater market share. It’s the unique value proposition that attracts customers and makes a company’s offerings more desirable than those of its competitors. This advantage can stem from various sources, and its sustainability depends on the ability of the company to maintain and leverage those sources effectively.Competitive advantage directly translates into superior financial performance.
Companies with a strong competitive advantage typically enjoy higher profit margins, increased revenue growth, and stronger market capitalization. This is because they can command premium prices, achieve higher sales volumes, and experience lower costs compared to their competitors. For instance, a company with a significant cost advantage can undercut its rivals on price, leading to increased market share and higher profits, even if profit margins per unit are lower.
Conversely, a company with a strong differentiation advantage can charge a premium price for its unique offerings, resulting in higher profit margins.
Types of Competitive Advantages
Competitive advantages fall into several key categories, each requiring a different strategic approach.
- Cost Advantage: This involves producing goods or services at a lower cost than competitors. This can be achieved through economies of scale, efficient operations, access to cheaper raw materials, or technological advancements. For example, Walmart’s vast logistical network and efficient supply chain give it a significant cost advantage in the retail sector.
- Differentiation Advantage: This strategy focuses on offering products or services that are perceived as unique and superior to competitors’ offerings. This uniqueness can be based on features, quality, branding, customer service, or other factors. Apple, for example, has built a strong differentiation advantage based on its brand image, design, and user experience.
- Innovation Advantage: This involves developing and introducing new products, services, or processes that competitors cannot easily replicate. This requires significant investment in research and development and a culture of innovation. Tesla’s pioneering work in electric vehicles and battery technology provides a prime example of innovation advantage.
Interconnectedness of Competitive Advantage Elements
Imagine a three-dimensional pyramid. The base represents the foundational elements: efficient operations (lean manufacturing, optimized supply chains), strong brand reputation (customer loyalty, positive brand perception), and access to resources (raw materials, skilled labor, capital). The middle layer comprises the core competitive advantages: cost leadership, differentiation, and innovation. These build upon the foundational elements. The apex of the pyramid represents the ultimate outcome: superior profitability and sustained market leadership.
Each layer supports the one above it; a weak foundation leads to an unstable competitive advantage. For instance, a company with a strong brand (foundation) can leverage this to command premium prices (differentiation advantage) and achieve high profitability (apex). Conversely, a company with weak operations (foundation) will struggle to achieve cost leadership (middle layer), limiting its profitability (apex).
Sustaining Advantage Over Time

Maintaining a sustainable competitive advantage is a significant challenge for businesses in today’s dynamic marketplace. The constant evolution of technology, shifting consumer preferences, and the emergence of new competitors create a volatile environment where even the most successful companies can experience a decline. Successfully navigating these challenges requires a proactive and adaptable approach, focusing on innovation, continuous improvement, and a deep understanding of the competitive landscape.Maintaining a competitive edge requires more than simply achieving a temporary advantage; it demands a continuous effort to adapt and evolve.
Companies face several key obstacles in their quest for lasting dominance. These obstacles include intense competition from both established players and agile newcomers, rapidly changing technological landscapes that render existing strategies obsolete, and the unpredictable nature of consumer behavior and market trends. Overcoming these challenges necessitates a multifaceted strategy that prioritizes flexibility, innovation, and a commitment to long-term value creation.
Challenges in Maintaining Sustainable Competitive Advantage
Companies face numerous hurdles in sustaining their competitive edge. Intense rivalry from competitors, both domestic and international, necessitates continuous innovation and adaptation. Rapid technological advancements can quickly render existing products and processes outdated, demanding significant investment in research and development to remain competitive. Changes in consumer preferences, driven by factors such as evolving demographics and shifting social values, also pose a significant threat.
Finally, unforeseen external factors, such as economic downturns or geopolitical instability, can disrupt even the most well-laid plans. Successful companies anticipate and mitigate these risks through proactive planning and robust contingency strategies.
Strategies for Adapting to Change
Adapting to changing market conditions and technological advancements is crucial for long-term success. This involves a multi-pronged approach, including rigorous market research to identify emerging trends and anticipate future needs. Companies must foster a culture of innovation, encouraging experimentation and the development of new products and services. Strategic partnerships and acquisitions can provide access to new technologies and markets, accelerating the adaptation process.
Furthermore, cultivating a flexible and agile organizational structure allows for swift responses to unexpected changes. This agility extends to operational processes, allowing companies to quickly adjust production, marketing, and distribution strategies as needed.
The Importance of Innovation and Continuous Improvement
Innovation and continuous improvement are cornerstones of a sustainable competitive advantage. Innovation drives the creation of new products, services, and business models, differentiating a company from its rivals and creating new sources of value. This can range from incremental improvements to existing offerings to radical breakthroughs that redefine entire industries. Continuous improvement, on the other hand, focuses on optimizing existing processes and enhancing efficiency.
This involves identifying areas for improvement, implementing best practices, and utilizing data-driven decision-making to enhance performance. Both innovation and continuous improvement are iterative processes, requiring a commitment to ongoing learning and adaptation.
Examples of Companies That Have Lost Their Competitive Advantage
Several well-known companies have experienced declines, illustrating the challenges of sustaining a competitive advantage. Kodak, once a dominant force in photography, failed to adapt to the rise of digital technology, ultimately leading to its bankruptcy. Blockbuster’s inability to anticipate the shift to streaming services resulted in its demise. These examples highlight the importance of proactively identifying and responding to disruptive technologies and evolving consumer preferences.
A failure to adapt to these changes can lead to obsolescence and loss of market share, even for established industry leaders. The reasons for their decline often include a lack of foresight, resistance to change, and an inability to innovate effectively.
Ultimately, achieving and sustaining a competitive advantage requires a holistic and dynamic approach. It necessitates a thorough understanding of the competitive landscape, a commitment to continuous innovation, and the ability to adapt to changing market conditions. By leveraging valuable resources, developing unique capabilities, and implementing effective strategies, businesses can build a strong foundation for long-term success and profitability. The journey is continuous, requiring vigilance, adaptation, and a relentless pursuit of excellence.
The strategies Artikeld provide a roadmap, but the execution and refinement are uniquely determined by each organization’s specific context and capabilities.
FAQ Overview
What is the difference between a competitive advantage and a sustainable competitive advantage?
A competitive advantage simply means a firm outperforms its rivals. A
-sustainable* competitive advantage implies this outperformance is likely to persist over time due to barriers to imitation or substitution.
How can a company identify its core competencies for a sustainable competitive advantage?
Companies should analyze their internal resources and capabilities using frameworks like VRIN (Valuable, Rare, Inimitable, Non-substitutable) to pinpoint those that are uniquely valuable and difficult for competitors to replicate.
What role does innovation play in maintaining a sustainable competitive advantage?
Innovation is crucial for sustained advantage. It allows firms to create new offerings, improve existing ones, and adapt to changing customer needs and technological advancements, thus constantly reinforcing their competitive edge.
How can a small business compete with larger, established companies?
Small businesses can leverage niche market strategies, focus on superior customer service, build strong brand loyalty, and adopt innovative technologies to compete effectively. Agility and adaptability are key.